Introduction
The most common methods for extracting mustard oil from mustard seeds are physical pressing (screw pressing) and solvent extraction.
Physical pressing is mechanical squeezing of mustard seeds to extract mustard oil, cake residual oil content of 5–10%. To achieve higher oil yield, we usually use solvent extraction to reduce cake residual oil to less than 1%.
In this article, I will introduce you to the process of extracting mustard oil using solvent extraction step by step, include machines used in each step and their functions.
![Mustard seeds reception Mustard seeds reception]()
Step1: Mustard Seeds Reception and Storage
Harvested mustard seeds transport at oil mill, through first inspection (impurities, moisture, mildew), and then are sent to storage silos.
Machines Used:
Conveying equipment (such as bucket elevator, belt conveyor, screw conveyor): Transport mustard seeds from transport vehicles or receiving points to cleaning section and storage silo.
Storage silos/silos: Safe and dry store large quantities of mustard seeds, maintain raw material quality, and provide buffer for continuous production. Typically equipped with ventilation and temperature monitoring systems.
Step2: Mustard Seed Cleaning and Impurity Removal
Remove impurities from mustard seeds, such as stones, soil clumps, metal fragments, stems, weed seeds, dust, etc. Impurities not only affect oil quality but also damage subsequent equipment.
Machines Used:
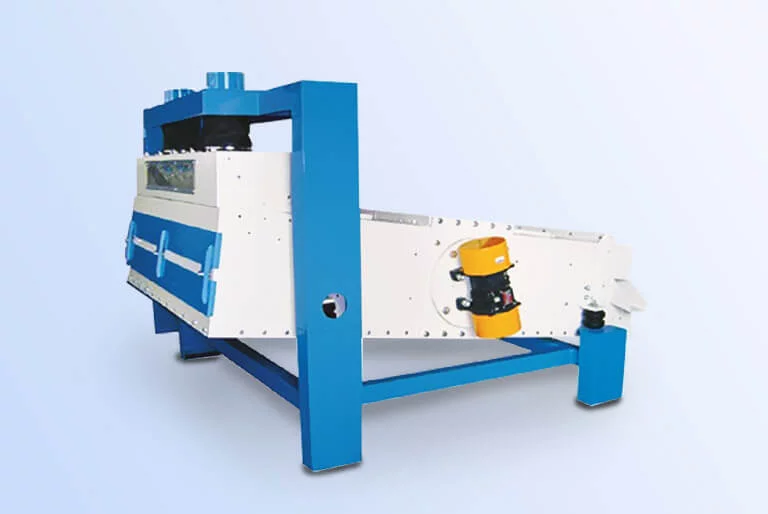
Vibrating screen: Utilize screens with different mesh sizes and vibration, separate impurities larger or smaller than mustard seeds (such as large stones, straw fragments, fine sand and dust).
![Mustard seeds vibrating screen Mustard seeds vibrating screen]()
Gravity grading destoner: Utilizes differences in material density and suspension speed, combined with airflow and vibrating screen plates, to effectively remove stones, mud clumps, and other heavy impurities that are similar in size to mustard seeds but have different densities.
Magnetic separator: Uses strong magnets to attract and remove ferromagnetic metal impurities (such as nails, screws, and iron fragments) from raw material, protecting subsequent equipment (especially oil press machine) from damage.
Air separator/dust extraction system: Uses airflow to separate lightweight impurities (such as dust, shriveled seeds, and some stems and leaves) and control workshop dust.
Special note: Mustard seed dust is explosive, so dust extraction system is very important.
Color sorter (optional): Uses optical principles to identify and remove moldy grains, discolored grains, and other impurities that affect color and flavor of mustard oil.
Step3: Mustard Seed Drying
If the moisture content of cleaned mustard seeds exceeds requirements for safe storage and pre-pressing, drying is necessary. Excessive moisture reduces oil yield, increases energy consumption, and promotes mold growth.
Machines Used:
Dryer: Uses hot air to reduce moisture content of mustard seeds under controlled conditions. Precise control of temperature and airflow is required to avoid overheating, which can affect oil quality.
Step4: Mustard Seed Crushing/Flaking
Crushing whole mustard seeds into small particles or flaking them into thin sheets (flakes). This step increases surface area exposed to oil, disrupts cell structure, and creates favorable conditions for subsequent steaming, roasting, and pre-pressing.
Machines Used:
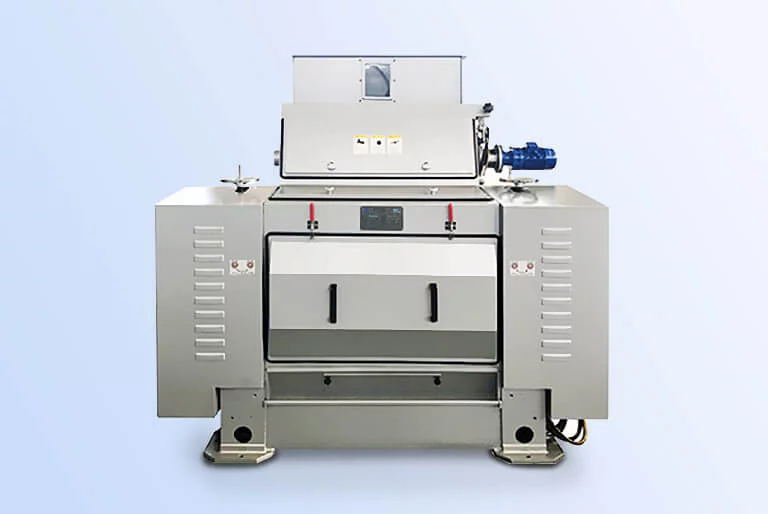
Crusher: (e.g., tooth roller crusher, hammer mill) to first crush seeds into several pieces.
Flaking machine: rolls crushed particles between a pair of smooth rollers into thin, uniform flakes (typically 0.2–0.4 mm thick). Ideal flakes should be thin without breaking and have minimal powder.
![Mustard seeds flaking machine Mustard seeds flaking machine]()
Step5: Mustard Seed Steaming/Conditioning
The rolled flakes are sent to steaming/roasting cooker and processed under controlled temperature, moisture, and time conditions.
Purpose of steaming/roasting:
- Adjust plasticity and elasticity of the flakes to make them more suitable for oil extraction.
- Coagulate oils (breaking bonds between oils and proteins, etc.).
- Reduce oil viscosity and improve flowability.
- Inactivate enzymes (such as myrosinase), reducing the formation of off-flavors (particularly important for mustard seeds, which contain glucosinolates that produce irritating compounds upon enzymatic hydrolysis).
- Control degree of protein denaturation.
Machines Used:
Steam roasting cooker (multi-layer vertical cooker most common): Features heating, stirring, moisture regulation, and residence time control functions. The multi-layer structure enables gradual heating, moisture removal, and maturation of the material. Typically equipped with sensors for temperature, moisture, and material level.
![Mustard seeds vertical cooker Mustard seeds vertical cooker]()
Step6: Mustard Seed Prepressing
Mustard seeds prepressing involve use 140 screw press machine to extract about 60–70% of oil from mustard seeds, resulting in a low-oil content pre-pressed cake (residual oil content of about 15–20%).
Purpose of prepressing:
- Reduce solvent consumption and recovery load: processing low-oil-content cakes is more economical than whole seeds.
- Enhance processing capacity of solvent extraction unit: cake structure is more porous, facilitating solvent penetration.
- Reduce residual oil in meal: residual oil content in prepressed cake is lower after solvent extraction.
- If the oil content of oilseed is very low, such as soybean, embryo can be directly extracted without prepressing. However, mustard seed has high oil content, and pre-pressing followed by solvent extraction is more efficiency process.
- Prepressed Cakes Crushing and Pelleting
- The cake gets from prepressing process is large and hard. They need to be crushed into particles of appropriate size. This step increase surface area exposed to solvent, thereby improve extraction efficiency.
Machines Used:
Crusher: Initially crushes large pieces of pre-pressed cake.
Pelletizer: Further processes crushed cake into sized particles suitable for extraction. Ensure particles are not too fine nor too coarse.
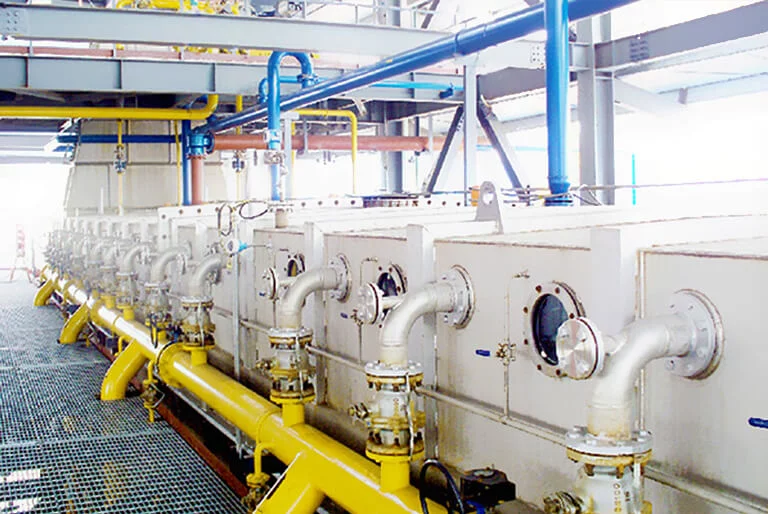
Step7: Solvent Extraction
The cake particles are fed into the extractor and come into countercurrent contact with the solvent (hexane). The solvent dissolves and carries away oils from cake particles, forming a mixed oil (a solution of oils and solvent). Cake particles that have undergone sufficient extraction are called wet cake and contain a large amount of residual solvent.
The core equipment for this step is extractor, which has three most common types:
![Henan Huatai Group rotocel extractor Henan Huatai Group rotocel extractor]()
A slowly rotating circular container. The meal particles continuously enter from top and are slowly pushed toward the center by rotating scrapers. Fresh solvent is sprayed near center and penetrates against direction of meal particle movement (toward the periphery).
Ultimately, newly added meal particles encounter high-concentration mixed oil, while wet meal about to be discharged encounters fresh solvent. Mixed oil is collected from feed end, wet meal is discharged from other end.
![Henan Huatai Group loop type extractor Henan Huatai Group loop type extractor]()
Features a ring-shaped stainless steel grid plate channel, with material conveyed via a scraper chain belt. The design include pre-leaching section, main leaching section, and drainage section, equipped with solvent spray system and V-shaped self-cleaning grating.
Leached meal particles are conveyed into leaching tank by scraper conveyor. Once tank reaches a certain material level, leaching tank begins operation as indicated by level sensor, and the material automatically enters upper horizontal spray section of leaching tank.
The material is first sprayed with higher concentration of mixed solvent, then passes through curved section and lower spray section. It is then sequentially sprayed with mixed solvent of decreasing concentration.
Before entering the drying section, it is sprayed with fresh solvent. The dried wet meal is discharged from bottom of extractor and ultimately conveyed to steam stripper via wet meal scraper conveyor.
![Henan Huatai Group drag chain extractor Henan Huatai Group drag chain extractor]()
The drag chain extractor spray pipes distributed on upper layer, and spray sequence gradually increases in concentration.
First, the upper layer receives 3–4 sprayings of mixed oil, with concentrations distributed in a gradient from high to low, completing main extraction.
Then, as material reaches the end, combing rods loosen the material layer and it falls to the lower layer, continuing to receive low-concentration mixed oil sprayings.
Finally, material is rinsed with fresh solvent to ensure residual oil in meal is ≤1.0%.
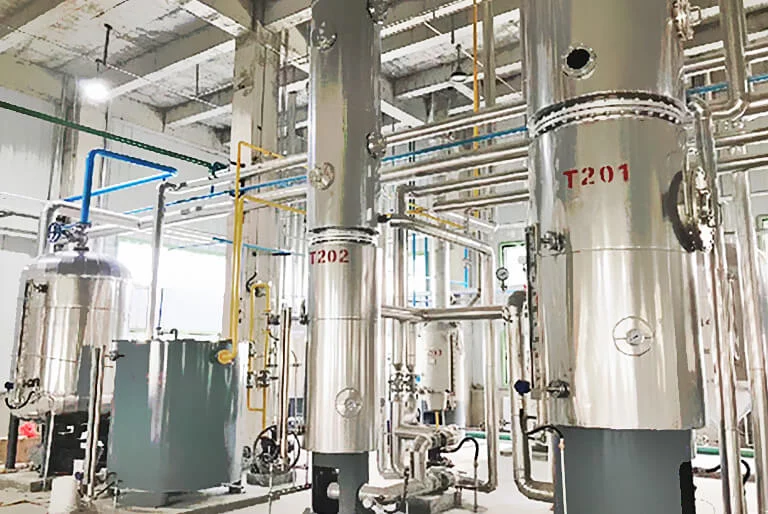
Step8: Mixed Oil Processing (Evaporation and Stripping)
The mixed oil exiting extractor (with about 20–30% oil content) contains a large amount of solvent, must separate and recovery to obtain crude extraction oil. This process consists of two steps:
Evaporation: Utilizing the property solvent boiling point is lower thanoil, most of the solvent is evaporated through heating. Typically, use multi-effect evaporation system, the secondary steam from later-stage evaporator heats earlier-stage evaporator, improve energy efficiency.
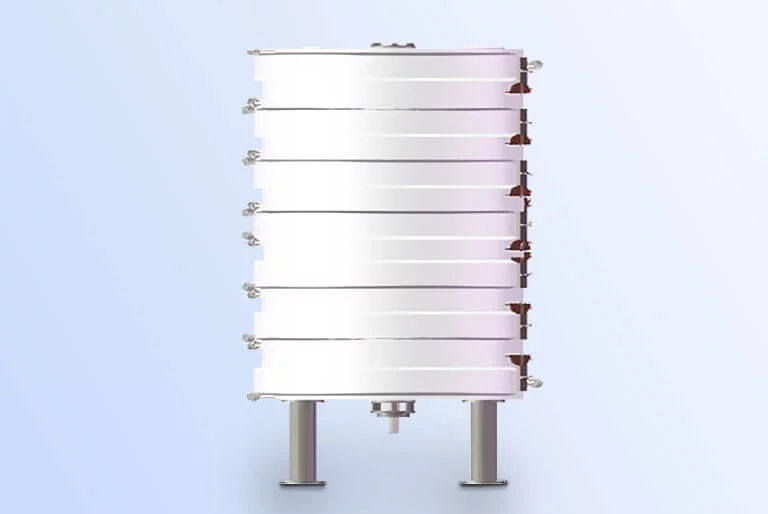
Stripping: The concentrated mixed oil (oil content about 90-95%) after evaporation still contains small amount of solvent. By injecting direct steam (stripping steam) into oil under vacuum conditions, the remaining solvent is further stripped out.
Machines Used:
Mixed oil storage tank/preheater: Stores mixed oil and preheats it via heat exchange.
First-effect evaporator: Use steam to heat mixed oil, causing it to boil and evaporate most of solvent.
Second-effect evaporator: Use steam generated by first-effect evaporator as heat source to further evaporate solvents from mixed oil.
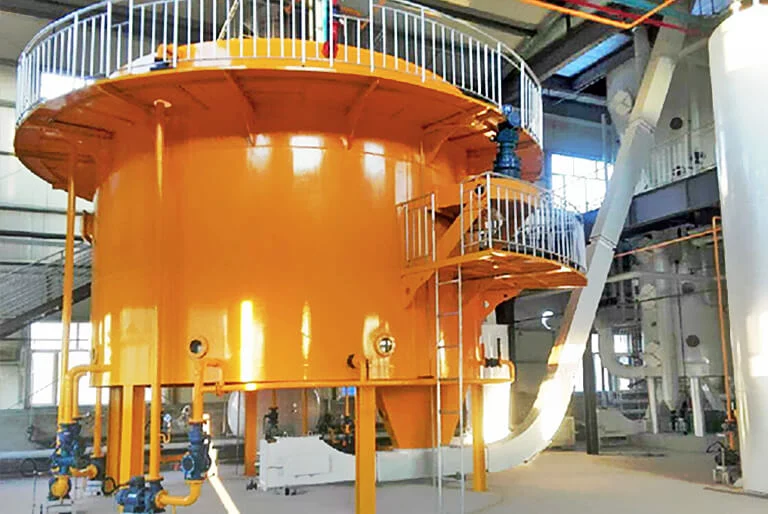
Stripping tower: Under combined action of vacuum and direct steam, the remaining small amount of solvent (typically <0.5%) in concentrated mixed oil is completely removed, get crude oil.
![Henan Huatai Group stripping tower Henan Huatai Group stripping tower]()
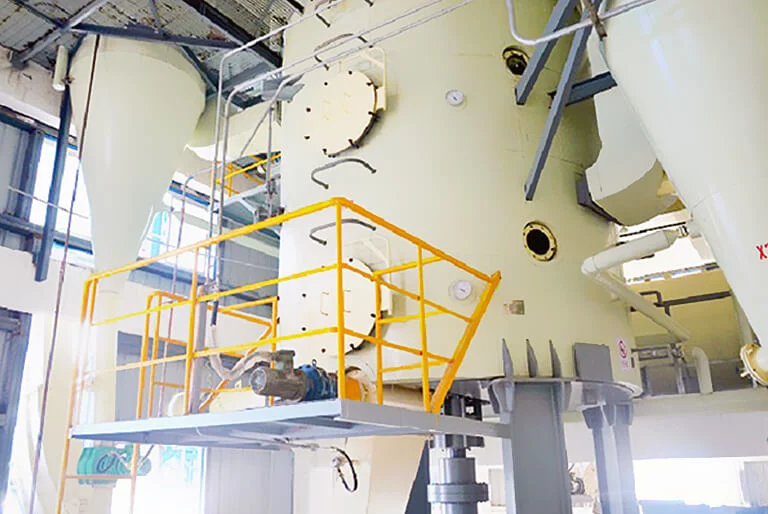
Step9: Wet Meal Desolventization
The wet meal from extractor contains 25–35% solvent. To get safe, feed-grade desolventized meal, solvent must be efficiently and thoroughly remove. At the same time, roasting destroy antinutritional factors (such as glucosinolates and myrosinase in mustard seed) and adjusts moisture content.
Machines Used:
DTDC desolventizer toaster: This is key equipment that integrates desolventizing, toasting, drying, and cooling functions. It typically has a multi-layer vertical structure (4-6 layers).
Top layer (desolventizing layer): Direct steam and a small amount of indirect steam are introduced to evaporate most of solvent at lower temperature (~70°C).
Middle layer (toasting layer): Indirect steam is introduced for heating, maintaining a higher temperature (100-110°C or higher) for a certain period, destroy antinutritional factors, sterilize, and remove unpleasant odors.
Bottom Layer (Drying/Cooling Layer): Hot air (drying layer) and cold air (cooling layer) are introduced to adjust moisture content of the meal to standard level (typically 10-12%) and cool it to near room temperature (below 40°C).
![Henan Huatai Group DTDC desolventizer toaster machine Henan Huatai Group DTDC desolventizer toaster machine]()
Step10: Solvent Recovery System
This is core component of the solvent extraction plant, running throughout entire process to ensure safe and efficient reuse of solvents. It is to maximize solvent recovery while minimizing losses (controlled below 0.5–1.5 kg per ton of raw materials).
Machines Used:
Condenser: Condenses solvent vapor from extraction units, evaporators, stripping towers, DTDC units, etc.
Separator: Separates recovered solvent from wastewater in condensate.
Solvent tank: Stores fresh solvent and recovered solvent, provide buffer for system. Typically consists of multiple tanks (fresh tank, circulation tank, waste solvent tank, etc.).
Solvent pump: Transports solvents between process sections.
Waste gas recovery system: Recovers waste gas containing trace amounts of solvents emitted from various parts of the processing system (e.g., water separator exhaust, tank breathing gas, vacuum pump exhaust, etc.).
Step11: Crude Mustard Seed Oil Refining
This is a necessary step in solvent extraction process! Although the solvent residue in the extracted mustard seed crude oil is extremely low (<50 ppm, or even lower), it contains phospholipids (gums), free fatty acids, pigments (chlorophyll, carotenoids), waxes, trace metals, volatile odor substances, residual trace solvents, and oxidation products or polymers that may be generated during extraction process.
The purpose of refining is to remove these impurities, improve stability, safety, color, flavor, and smoke point of mustard seed oil, and meet food or industrial standards.
![Small scale mustard oil refining machine Small scale mustard oil refining machine]()
Mustard seed oil refining steps:
- Degumming: Remove phospholipids and other colloidal impurities (by hydration or acidification).
- Neutralization: Remove free fatty acids (commonly using alkali refining).
- Decolorization: Removal of pigments (using white clay/activated carbon adsorption).
- Deodorization: Distillation under high vacuum and high temperature to remove off-flavor substances, residual free fatty acids, trace solvents, oxidation products, etc.
- Dewaxing/Winterization: Removal of waxes and high-melting-point glycerides that precipitate at low temperatures (to keep oil clear at low temperatures).
Equipment used: Refining tanks/reactors, centrifuges, decolorization towers, leaf filters, deodorization towers (with high-vacuum systems and fatty acid capture systems), heat exchangers, coolers, crystallization tanks, growth tanks, winterization filters, polishing filters, etc.
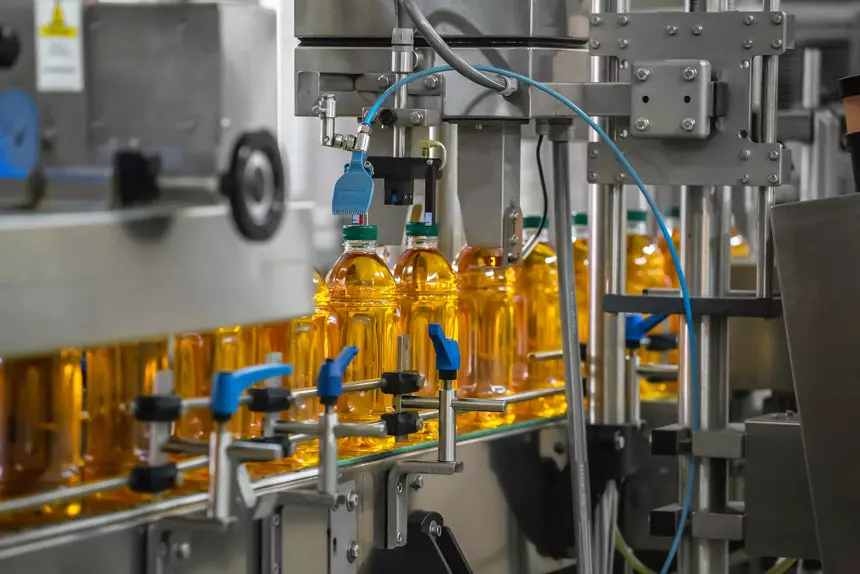
Step12: Mustard Seed Oil Storage and Packaging
Refined mustard seed oil must be stored in a light-protected, low-temperature (or room-temperature) environment with nitrogen flushing to prevent oxidation and spoilage. It is then bottled.
Equipment used: finished oil storage tanks, bottling machine, capping machine/sealing machine, labeling machine/inkjet printer, packing machine, etc.
![Mustard seed oil bottling machine Mustard seed oil bottling machine]()
Conclusion
In general, there are two methods to extract mustard oil from mustard seeds: physical pressing and solvent extraction.
The core process of physical pressing method: cleaning, drying, crushing/rolling, steaming, pressing, filtering, cake processing, refining and storage packaging.
The core process of solvent extraction method: prepressing cake, extraction, mixed oil processing, wet meal desolventization, solvent recovery, refining and storage packaging.
Henan Huatai Intelligent Equipment Group has many years of experience in mustard oil extraction equipment and can provide customized solutions for these two different mustard oil extraction methods. If you are interested in buying mustard oil processing machine or opening mustard oil production line, please contact us for a free quote!
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ