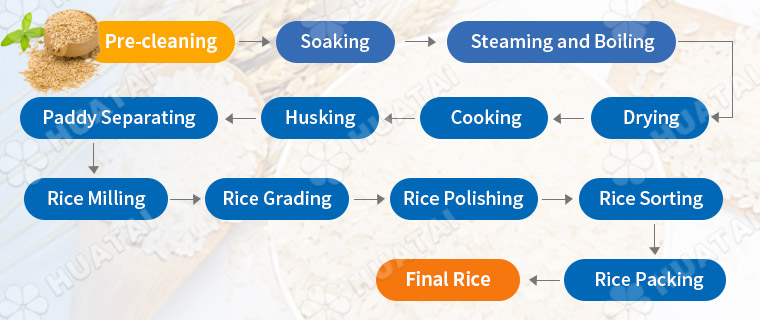
Rice Parboiling Section:
Raw Paddy → Pre-Cleaning → Soaking → Steaming and Boiling → Drying → Cooling → To Rice Milling
Rice Milling Section:
Parboiled Paddy → Husking and Separating → Rice Milling →Rice Polishing and Grading → Rice Color Sorting → Rice Packing
Paddy Cleaning: In this stage we remove the impurities from the paddy.
The rice should be cleaned first to remove the straw, stones, hemp rope, other large debris and impurities such as dust mixed into the rice.
Paddy Soaking: The aim of soaking is making paddy absorb enough water, create conditions for starch pasting. During the course of starch pasting paddy must absorb above 30% water, or it will not be able to fully steam the paddy in next step and thus to influence the quality of rice.
a. Through vacuuming, constant temperature, and pressure soaking, the water is fully absorbed by the rice in a short time, so that the water content of the rice reaches more than 30%, which is a necessary condition for the rice starch to be fully gelatinized during the cooking process. In the parboiled rice production line, this processing section is the basic and important section.
b. Depending on the variety and quality of rice, the soaking temperature is usually 55-70 degrees, and the soaking time is 3.5-4.5 hours.
 Steaming and Boiling
Steaming and Boiling: After soaking the inside of endosperm has got enough water, now it’s time to steam the paddy to realize starch pasting. Steaming can change the physical structure of rice and keep the nutrition, to increase the production ratio and make rice easy to store.
Parboiled Paddy Drying: The aim of drying is to make moisture reduced from around 35% to around 14%, to reduce moisture can make the rice easy to store and transport, and greatly increase the production ratio, as the maximum whole rice rate can be obtained when rice is milled.
Parboiled Paddy Cooling: The dried paddy is sent to vertical storage for temporary storage so that it is fully slowed down and cooled before being processed. The vertical cylinder warehouse is equipped with a ventilation fan, which can take out the remaining heat. And make the rice moisture evenly.
Rice Husking and Separation: Using the rice hulling machine to remove the husk of dried paddy. After soaking and steaming it will be very easy to husk the paddy and save energy.
The paddy separator is mainly used for separating brown rice from paddy by their differences in specific gravity and friction coefficient in three parts: paddy, brown rice, and a mix of both.
Rice Milling: The pearling of parboiled rice cost much more time than normal paddy. The reason is that after soaking the rice is easy to become smectic. In order to avoid this problem, we use blowing rice miller and increase the rotating speed of rice miller, the rice bran transmission adopt pneumatic type to reduce the friction.
Rice Polishing: The rice polishing process is to polish the rice surface by spraying water, which facilities the formation of a smooth gelatinous layer that prolongs the preservation time. Extended polishing chamber to produce high-quality rice. Good rice come through the polishing machine, it will make the milling rice become more beautiful color and glossy, thus to increase the quality of rice.
Rice Grading: Rice grading machine is used to sieve the milled rice efficiently and accurately into several classes: head rice, large broken, medium broken, small broken, etc.
Rice Color Sorting: The rice we get from above step still has some bad rice, broken rice or some other grains or stone. So here we use color sorting machine to select the bad rice and other grains.
Color sorting machine is an important machine to ensure we can get high quality rice. Using the rice color sorting machine to sort the bad, milky, chalky, paddy, and foreign materials out.
Finished Rice Packing: The finish rice now is ready dear all! Let's use our automatic weighing and packing machine to make them into 5kg 10kg or 50kg bags.
It can be seen from the processing process of parboiled rice that the production process of a full set of the paddy parboiling plant is based on the processing technology of white rice, adding hydrothermal treatment processes such as soaking, steaming and boiling, drying and cooling, and slow stewing.
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ















