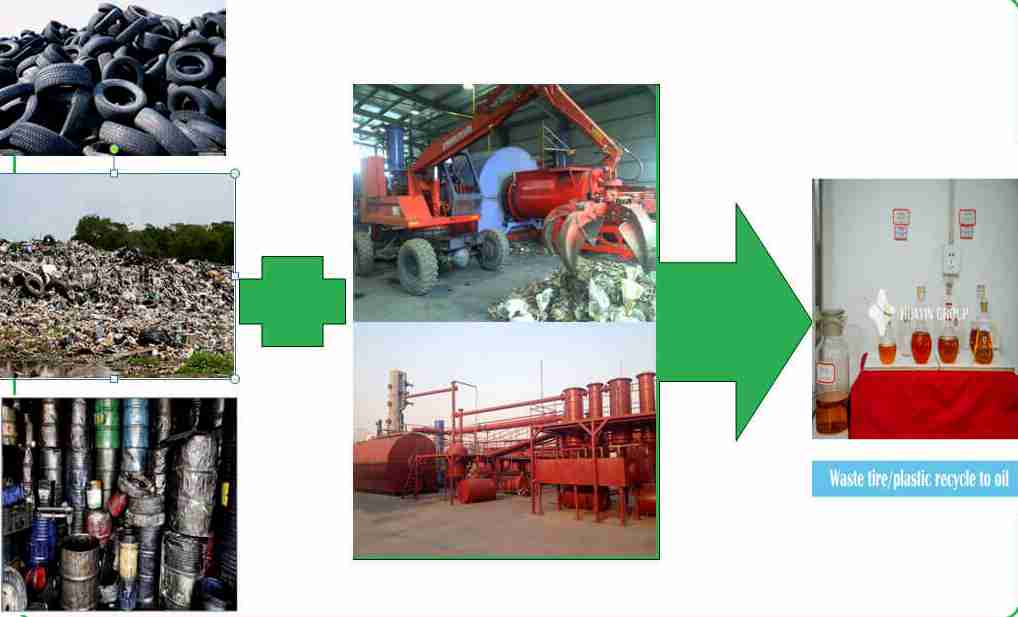
Henan Huatai Cereals and Oils Machinery Co., Ltd., leveraging its extensive experience in industrial thermal processing and equipment manufacturing, proudly presents its advanced semi-continuous tire pyrolysis system. This technology embodies our commitment to innovative, sustainable, and efficient resource recovery solutions. The video demonstrates a typical workflow, and this article details the refined engineering behind the process.
Step 1: Automated Feeding & System Preheating
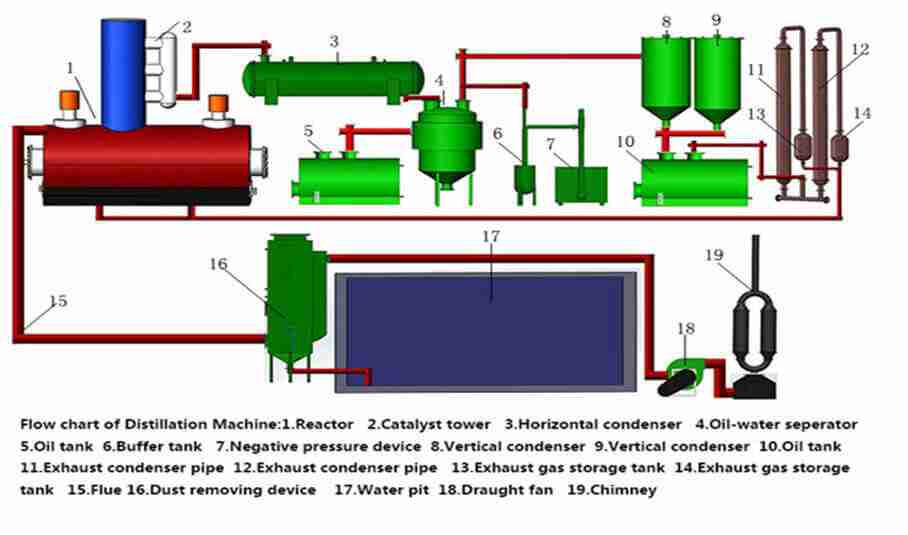
The process begins with uniformly crushed tire rubber powder, a critical preparation step for efficient thermal breakdown. This material is automatically conveyed via a sealed feed hopper and a specially designed high-temperature ball valve system into the pyrolysis reactor. This setup ensures an airtight seal, preventing oxygen ingress and maintaining optimal reaction conditions. Once loaded, the integrated burner system ignites, heating the furnace jacket surrounding the reactor to initiate the thermal process.
Step 2: Controlled Pyrolysis Reaction
Inside the horizontally mounted reactor, internal spiral scrapers or pushers gently but continuously advance the rubber material. This design ensures uniform heat transfer from the reactor walls, preventing hot spots and promoting consistent decomposition. As the material temperature rises through the critical pyrolysis range (typically 300-450°C), the long polymer chains in the rubber break down through thermal cracking. This controlled decomposition converts the waste tires into three primary products: hydrocarbon vapors (pyrolysis oil gas), solid carbon black, and non-condensable gas.
Step 3: Efficient Vapor Condensation & Gas Recycling
The hydrocarbon vapors produced are immediately piped into a multi-stage condensation system. The system showcased often includes a high-efficiency water-tank condenser. Here, circulating cooling water rapidly extracts heat from the vapors, causing them to condense into liquid pyrolysis oil, which is then collected for further refinement or use. The remaining non-condensable gas, primarily composed of lighter hydrocarbons, is not wasted. It is first routed through a tail gas treatment system—such as a desulfurization and deodorization unit—to remove pollutants. The cleaned gas is then redirected to fuel the main reactor burner, creating a closed-loop energy recovery system that significantly reduces external fuel requirements and enhances overall energy efficiency.
Step 4: Solid Residue Handling: Carbon Black Discharge & Cooling
The solid residue, carbon black, accumulates at the reactor's discharge end. It is periodically and automatically removed through another high-temperature sealing ball valve. This prevents air leakage back into the reactor. The hot carbon black then enters a dedicated cooling system, often a rotary cooler, where it is safely and efficiently cooled to near ambient temperature. The cooled, inert carbon black is finally collected for bagging. This high-quality carbon black can be sold as a commercial product for use in various industries, such as rubber manufacturing or as a pigment.
Technical Advantages of the Huatai Semi-Continuous System
Huatai's semi-continuous design ingeniously bridges the gap between different technological approaches:
Operational Efficiency & Environmental Performance: Like fully continuous plants, it offers superior environmental control through sealed, automated operation and efficient gas recycling, minimizing emissions.
Economic Flexibility & Lower CAPEX: It retains the lower initial investment cost and operational flexibility associated with batch systems, making it an accessible and scalable solution for many operators.
Huatai Engineering Quality: Built with robust materials and incorporating Huatai's decades of thermal processing expertise, the system ensures durability, safety, and consistent output.
This tire pyrolysis system is a testament to Huatai's philosophy of converting waste challenges into valuable opportunities, contributing to a circular economy.
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ










