The role and importance of grain dryers
The main role of
grain dryers is to remove excess moisture from harvested grains to reduce the risks of mildew, germination and pests, and ensure that grains can be stored safely. Grains with too high moisture content will not only reduce their nutritional value, but also easily become mildewed, thereby contaminating food and affecting human health. Therefore, the use of grain dryers can effectively extend the shelf life of grains and increase their market value.
In modern agricultural production, grain production has increased year by year, but at the same time, climate change and extreme weather have also brought many challenges. For example, during the harvest season, sudden rainy weather may cause grains to become damp. At this time, the role of grain dryers is particularly prominent. It can quickly and effectively dry wet grains to the ideal moisture content to maintain their quality.
Working principle of grain dryers
The working principle of grain dryers is based on the basic principles of heat conduction and heat convection. Hot air is generated inside the equipment through a heat source (such as a boiler, hot air furnace, etc.), and then circulated and blown into the grains, evaporating the moisture in the grains through convection. Specifically, the drying process can be divided into the following stages:
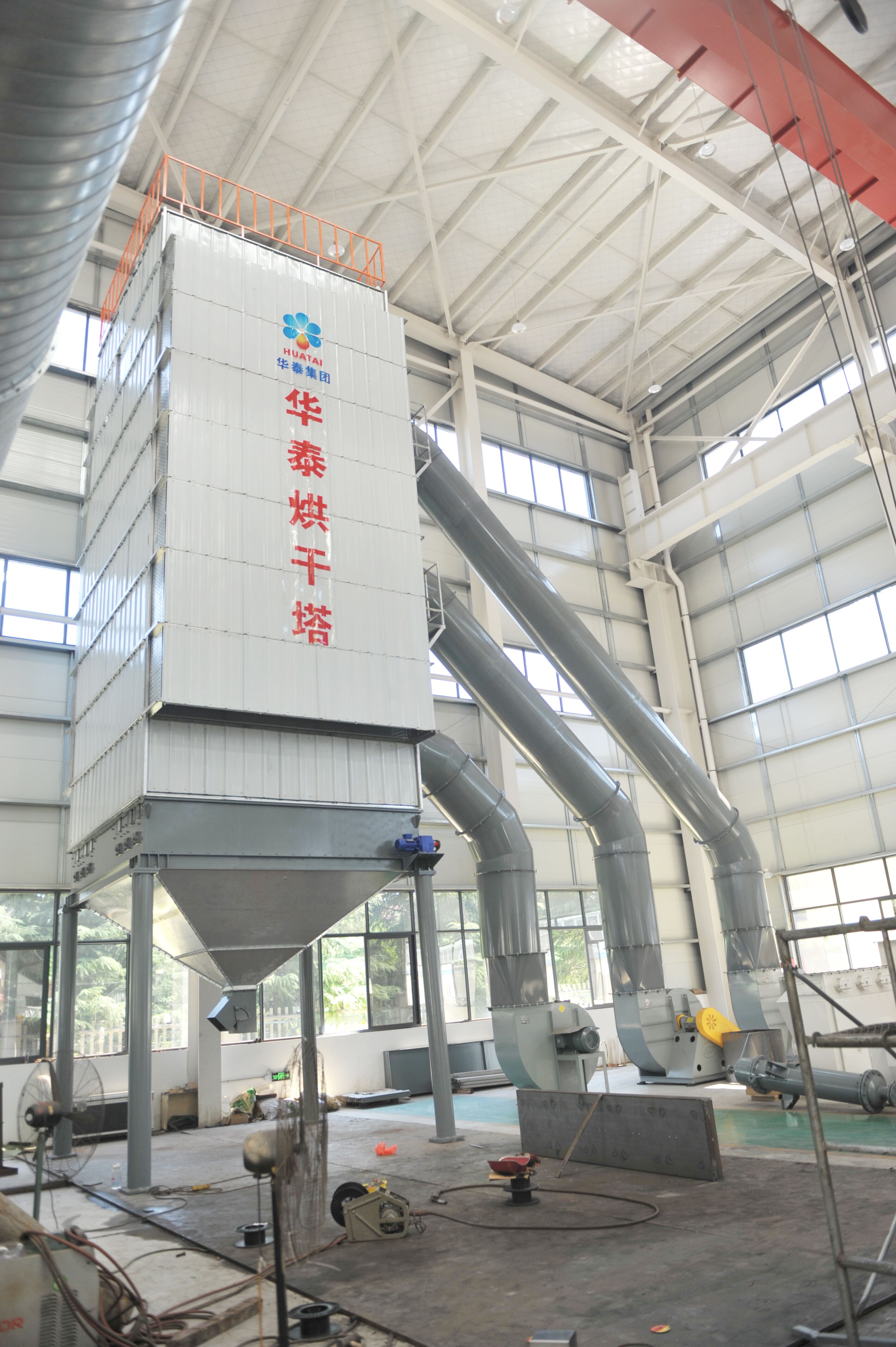

1.
Preheating: The grain will go through a preheating stage before entering the dryer, at which time the internal temperature rises slightly to prepare for subsequent drying.
2.
Drying stage: Through the circulation of hot air, the moisture in the grain is gradually evaporated. During this process, as the moisture evaporates, the temperature of the grain will rise.
3.
Cooling stage: After drying, the grain needs to be cooled to prevent quality degradation caused by high temperature and reduce the risk of mildew during storage.
4.
Storage stage: When the grain reaches the ideal moisture content, it is sent to the storage device to ensure that it will not be affected by moisture during storage.
Types of grain dryers
According to different uses and drying requirements,
grain dryers can be divided into many types:
1.
Hot air dryer: Use hot air circulation to dry grain. This dryer has a simple structure and is easy to operate. It is suitable for small and medium-sized grain drying.
2.
Fluidized bed dryer: uses airflow to suspend small grains in the air, and achieves rapid drying through full contact with hot air. This type of dryer is usually suitable for processing small and uniform grains.
3.
Rotary dryer: uses a rotating cylinder to continuously turn the grains, thereby increasing the contact area with hot air and improving drying efficiency. This type of equipment is suitable for processing bulk grains.
4.
Vacuum dryer: reduces the boiling point of water by reducing air pressure, thereby achieving gentle drying. This dryer is suitable for grains that are sensitive to temperature (such as some special varieties of grains).
5.
Hybrid dryer: combines multiple drying technologies, has strong adaptability, and can meet the drying needs of different grains.
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ