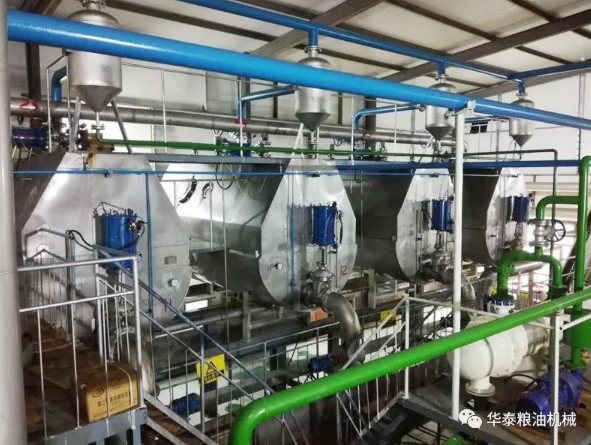
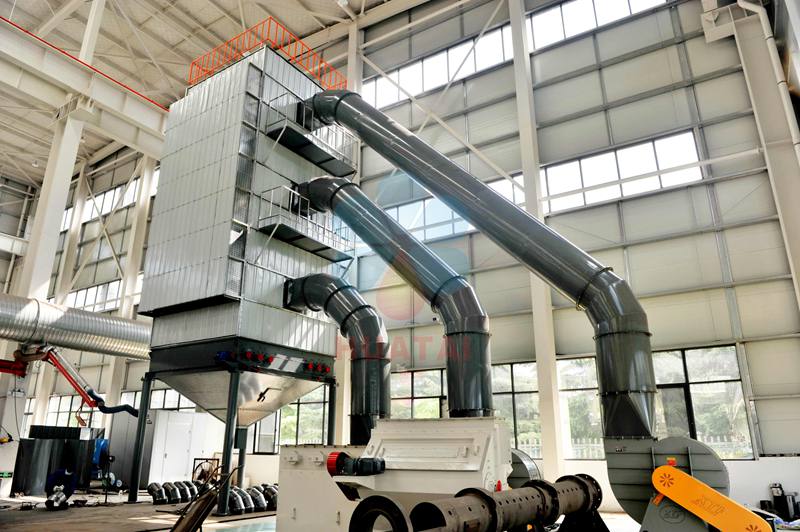
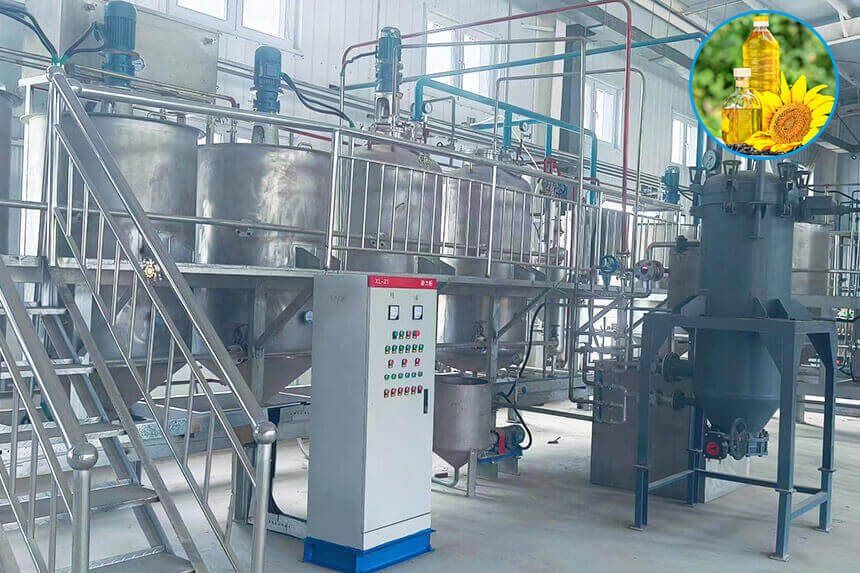
The extraction process of avocado oil (avocado oil) varies according to the extraction method. Common extraction methods include cold pressing,
solvent extraction, aqueous enzyme method, supercritical fluid extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, ultrasound-assisted extraction, etc. The following are the process flows of several main methods:
1. Cold pressing method (traditional method)
Process flow:
Raw material pretreatment: Select mature, pest-free avocado fruits, remove the core and skin after washing, and take the pulp.
Crushing and pressing: The pulp is broken into small pieces and pressed at low temperature (usually below 50) by mechanical pressing (such as a screw press) to separate the oil from the pulp.
Filtration and refining: The crude oil squeezed out is filtered, precipitated and other steps to remove impurities to obtain refined avocado oil.
Features:
Advantages: Simple operation, no chemical solvents required, the nutrients of the oil are intact, and the oxidation stability is good.
Disadvantages: Low oil yield and high residual oil content.
2. Solvent extraction method
Process flow:
Raw material pretreatment: Dry the avocado pulp to a certain moisture content (usually less than 10%) to facilitate solvent penetration.
Solvent extraction: Mix the dried pulp with an organic solvent (such as n-hexane) and stir at an appropriate temperature to dissolve the oil in the solvent.
Evaporation and recovery: Remove the solvent by evaporation to obtain crude oil; the solvent is recycled after recovery.
Refining: The crude oil undergoes steps such as degumming, deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization to obtain refined avocado oil.
Features:
Advantages: High oil yield, suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Disadvantages: Organic solvents are required, there may be a risk of solvent residues, and high-temperature treatment may lead to loss of nutrients.
3. Aqueous enzyme method
Process flow:
Raw material pretreatment: Crush the avocado pulp into a pulp.
Enzymatic hydrolysis: Add biological enzymes such as pectinase and cellulase, and perform enzymatic hydrolysis under appropriate temperature and pH conditions to destroy the cell wall structure and release oil.
Separation: The oil-water mixture is separated by centrifugation or filtration, and then the oil is obtained by standing or centrifugation.
Refining: The oil is dehydrated, degummed, decolorized and other steps to obtain refined avocado oil.
Features:
Advantages: mild reaction conditions, high oil quality, no solvent residue.
4. Supercritical fluid extraction method
Process flow:
Raw material pretreatment: Dry and crush the avocado pulp.
Supercritical extraction: Use supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO₂) as solvent to extract oil under high pressure (usually 20-40 MPa) and suitable temperature (35-50).
Separation: Carbon dioxide is separated from oil by decompression or heating to obtain crude oil.
Refining: The crude oil is degummed, deacidified, decolorized and other steps to obtain refined avocado oil.
Features:
Advantages: high extraction efficiency, good oil quality, no solvent residue, environmental protection.
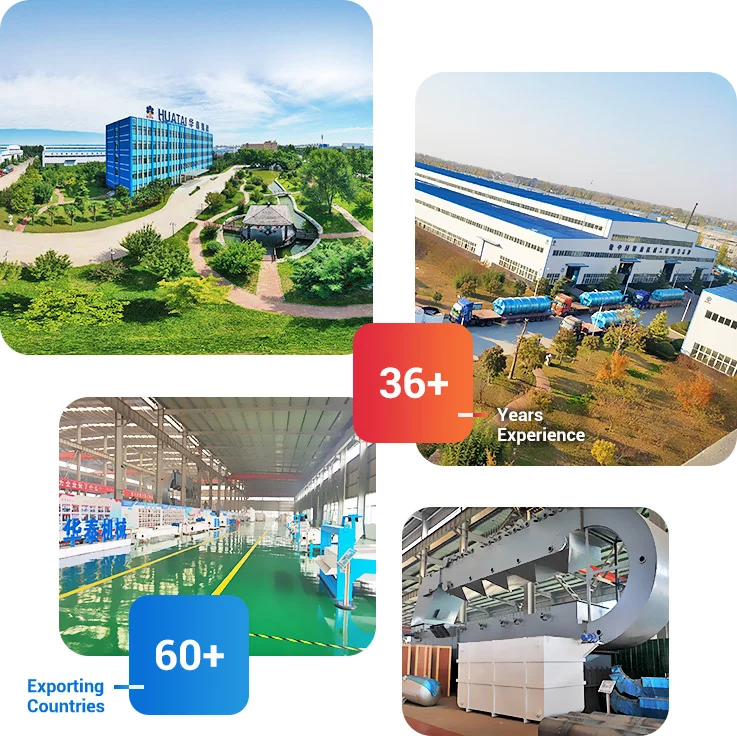
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ

 The extraction process of avocado oil (avocado oil) varies according to the extraction method. Common extraction methods include cold pressing,
The extraction process of avocado oil (avocado oil) varies according to the extraction method. Common extraction methods include cold pressing,