Introduction
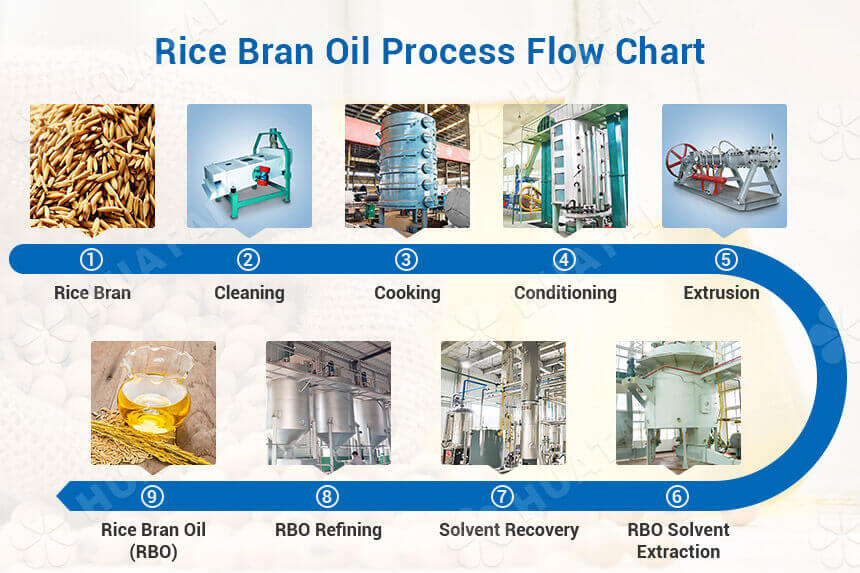
The rice bran oil (RBO) extraction process involves cleaning, cooking, conditioning, extrusion, solvent extraction, solvent recovery, and refining. Next, I will introduce you to step by step in detail.
Step 1: Rice Bran Cleaning
First, remove all impurities that affect rice bran oil yield, equipment lifespan, and oil quality, such as rice husks, broken rice, straw, sand, and metal fragments. The cleaning process involves four stages:
- Initial cleaning: A rotating cylindrical screen removes large impurities from the rice bran.
- Air separation: An air separator removes lightweight rice husks.
- Magnetic separation: A magnetic separator thoroughly adsorbs ferrous metal.
- Fine screening: Flat rotary screens or vibrating screens separate broken rice of similar size.
Huatai Group using a three-layer cleaning system, achieving impurity removal efficiency ≥99.5%.
Step 2: Rice Bran Cooking
The cooking process uses wet heat treatment to denature and deactivate enzymes and proteins completely. Inside the cooking pot, indirect steam heats rice bran to 85-90℃, and direct steam injection adjusts moisture content to 14-16%.
Step 3: Rice Bran Conditioning
After cooking, rice bran enters a conditioning tower where it stays at 100-110℃ for 20-30 minutes. This process uniformly distributes moisture, temperature, and maturity throughout the material. (Watch Video: Vietnam rice bran oil production line project video >>)
This step completely denatures and coagulates proteins, thoroughly breaking down oil cell structure, and facilitates the next expansion.
Huatai Group uses a three-dimensional precision control system for temperature, moisture, and time, ensuring each rice bran particle receives uniform heat treatment. Our system achieves enzyme deactivation rates ≥99.9%, and processed rice bran acid value increases are controlled within 1 mgKOH/g over 24 hours.
![Rice bran oil extraction machine for sale Rice bran oil extraction machine for sale]()
Step 4: Rice Bran Extrusion
The expansion process transforms powdered rice bran into porous granular material, improving permeability and reducing solvent residue. The expansion process includes three stages:
- High-temperature treatment: Conditioned rice bran enters the expander, screw shaft compression and friction rapidly raise temperatures to 125-140℃.
- Expansion: High-temperature, high-pressure material extrudes through die holes, instantly releasing pressure. Internal moisture flash evaporates, forming porous expanded material (bulk density 450-550 g/L).
- Drying and cooling: High-temperature expanded material (about 8-10% moisture) immediately enters a drying cooler. Cool air penetrates the material layer, reducing temperature to 55-60℃ and moisture to 7-8%. This prevents caking and ensures safe, efficient extraction.
Huatai Group's patented layered extruder die head design reduces extraction residual oil ≤0.8% and improves solvent penetration speed by over 50% compared to traditional oil materials.
Step 5: Rice Bran Oil Solvent Extraction
Expanded rice bran enters a rotocel extractor or loop type extractor for countercurrent soaking extraction with solvent (n-hexane). (Related Post: Rice bran oil solvent extraction plant >>)
Fresh solvent sprays onto material with the lowest oil content, while progressively concentrated mixed oil (a solvent-oil mixture) countercurrently washes material with the highest oil content, ultimately producing concentrated mixed oil at 28-32% concentration.
Huatai Group's extractors use hydraulic drive systems and segmented grid floor designs, operating smoothly without dead zones. Wet meal solvent content stays low at 28-32%, and mixed oil suspended solids content remains below 0.02%, significantly reducing the load on subsequent evaporation systems.
![Rice bran oil solvent extraction plant project Rice bran oil solvent extraction plant project]()
Step 6: Solvent Recovery
This step recovers and recycles solvent from both mixed oil and wet meal, reducing costs. The solvent recovery process divides into mixed oil treatment and wet meal treatment:
Mixed Oil Treatment: Concentrated mixed oil through sedimentation and filtration before entering first evaporation, second evaporation, and stripping towers. Under gradually increasing temperature and vacuum conditions, the system completely evaporates and condenses the solvent for recovery, producing crude rice bran oil (CRBO) at temperatures ≤80℃.
Wet Meal Treatment: Wet meal enters the DTDC (desolventizing, toasting, drying, and cooling) system. Removes solvent through indirect steam heating and direct steam stripping, then dries and cools to produce finished meal (solvent residue ≤500ppm, temperature ≤40℃).
Huatai Group's negative pressure evaporation and low-temperature desolventizing process achieves solvent consumption ≤2.5 kg/ton of material (national standard: ≤5 kg), reducing steam consumption by 15%. This process maximally prevents protein denaturation in the meal, retaining its high nutritional value.
![Rice bran oil refining process with flow chart Rice bran oil refining process with flow chart]()
Step 7: Rice Bran Oil Refining Process
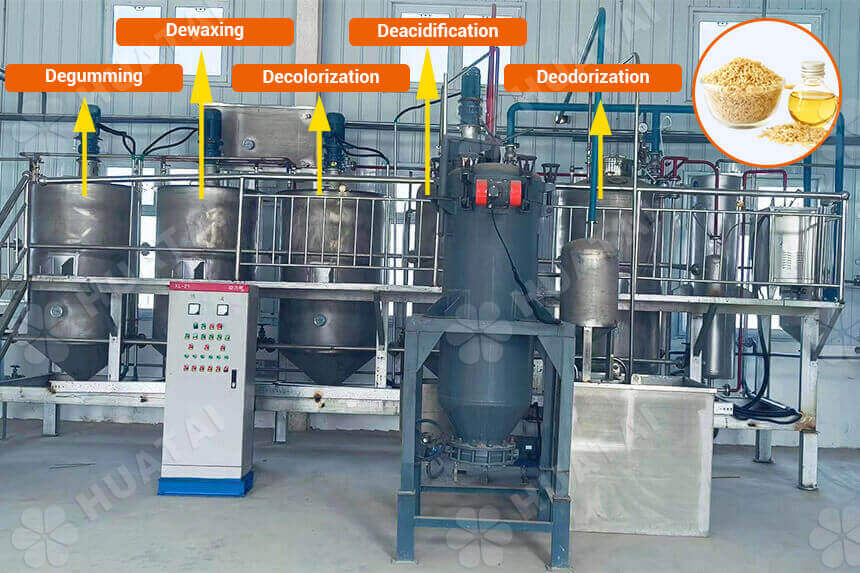
The rice bran oil refining process removes gums, waxes, pigments, free fatty acids, and off-flavors from CRBO, producing safe, stable, clear oil. Refining includes five stages:
- Degumming: The system heats CRBO to 70-80℃ and adds hot water and food-grade phosphoric acid, causing non-hydratable phospholipids and other gums to absorb water, coagulate, settle, and separate. Degummed oil contains phospholipid content below 50ppm.
- Dewaxing (Winterization): Rice bran oil contains 3-5% high-melting-point wax esters. After pre-cooling, degummed oil slowly cools to 5-10℃ in crystallization tanks and ages for 24-48 hours, allowing wax crystals to grow. Filtration equipment then removes wax at low temperature, ensuring the oil remains clear and transparent at low temperatures.
- Decolorization (Bleaching): In a vacuum bleaching tower, add activated clay (1-3%) dewaxed RBO at 105-110℃ to adsorb and remove chlorophyll, carotenoids, and other trace impurities.
- Deacidification: There are two methods for deacidification: physical deacidification and chemical alkali refining. Because RBO has a high acid value (AV>15), it using physical deacidification (steam distillation deacidification). Under high temperature (240-260℃) and high vacuum conditions, steam distillation removes free fatty acids. Compared to chemical alkali refining, this method improves oryzanol retention by over 30% and produces no soapstock.
- Deodorization: This is the final refining stage. Deacidified rice bran oil through treatment at 260-270℃ under pressure ≤2mbar with direct steam injection, thoroughly removing small aldehyde and ketone odor compounds and residual fatty acids, producing finished oil with pure flavor and high smoke point.
Conclusion
The above is the complete rice bran oil extraction process. By understanding these steps, you can get high-quality rice bran oil and maximize profits.
Henan Huatai Intelligent Equipment Group has over 38 years of experience designing and manufacturing complete rice bran oil production lines, from 10 tons to 1000+ tons per day capacity. Our turnkey solutions include equipment supply, installation, training, and technical support to ensure your operation runs efficiently.
Contact us today for a free consultation and discover why processors worldwide trust Huatai Group for their rice bran oil plant.
References:
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ