Introduction
Sesame oil come from nutrient-rich sesame seeds, rich in antioxidants, vitamin E, and healthy fats. Sesame oil extraction methods include water extraction, physical pressing, solvent extraction, and subcritical extraction.
Among them, physical pressing is highly efficient, high yield and low cost. Through pretreatment, steaming and roasting, pressing, refining, and packaging standard process, can achieve industrial-scale continuous production.
![Sesame oil production process Sesame oil production process]()
Step 1: Sesame Pretreatment - Cleaning and Conditioning
Screening and Remove Impurity
When raw sesame seeds arrive at processing factory, they contain various impurities, including stones, dust, plant debris, and damaged sesame seeds. These impurities need to remove.
Vibrating screen and magnetic separator remove stones, metal, and straw. Air separator blow away shriveled seeds and light debris.
This cleaning step protect processing equipment from damage and improve final sesame oil quality.
Water Washing and Moistening
The cleaned sesame seeds then need to wash.
The sesame seeds are washed with clean water in a rinsing tank, remove attached sand and dirt.
After draining, adjust moisture content to 8%-10%, prevent mold growth and ensure seeds do not become too brittle, thereby maximize oil yield.
![Sesame seed frying machine Sesame seed frying machine]()
Peeling and Shelling (Optional)
For higher-quality sesame oil, need to remove outer shells of sesame seeds. Hulling machine is used to remove shells (accounting for 15%-20% of seed weight), improve oil clarity and nutritional value.
Hulling machine have two methods: wet hulling and dry hulling.
- Wet hulling: Soak sesame seeds in sodium hydroxide hot water (50-60°C) for about 9 minutes, then stir remove seeds shells.
- Dry hulling: Use cylindrical hulling machine achieve a hulling efficiency of 99%.
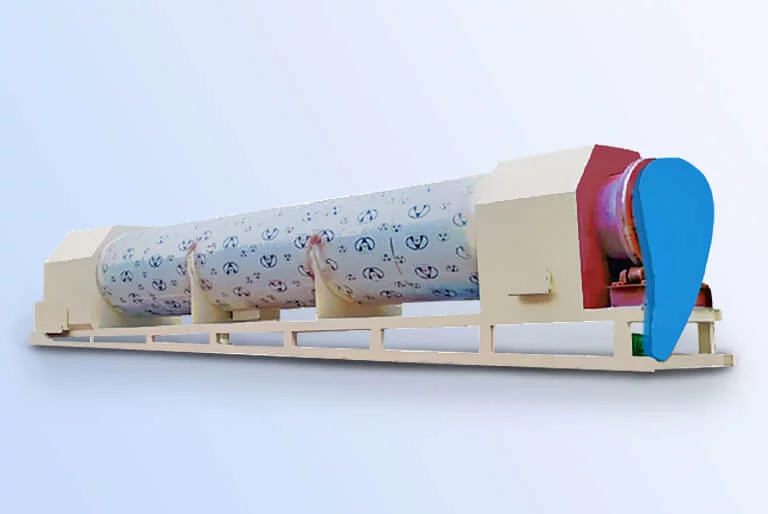
Step 2: Sesame Steaming and Frying - Remove Moisture
The second step is use vertical cooker to steam and fry sesame seeds, reduce moisture content and prepare for pressing.
The vertical cooker is divided into 5 layers, temperature gradually increases. The first layer temperature is 80-90℃, make sesame seeds evenly heated, control moisture content between 12%-14%. Second and third layers temperature is 100-110℃, seeds protein denatures, moisture content of 8%-9%. Fourth and fifth layers temperature is 125-130℃, make seeds mature and fragrant, moisture content is 4%-5%.
The steaming and frying time is controlled at 40-50 minutes, ensure highest oil yield during pressing.
![Sesame vertical cooker Sesame vertical cooker]()
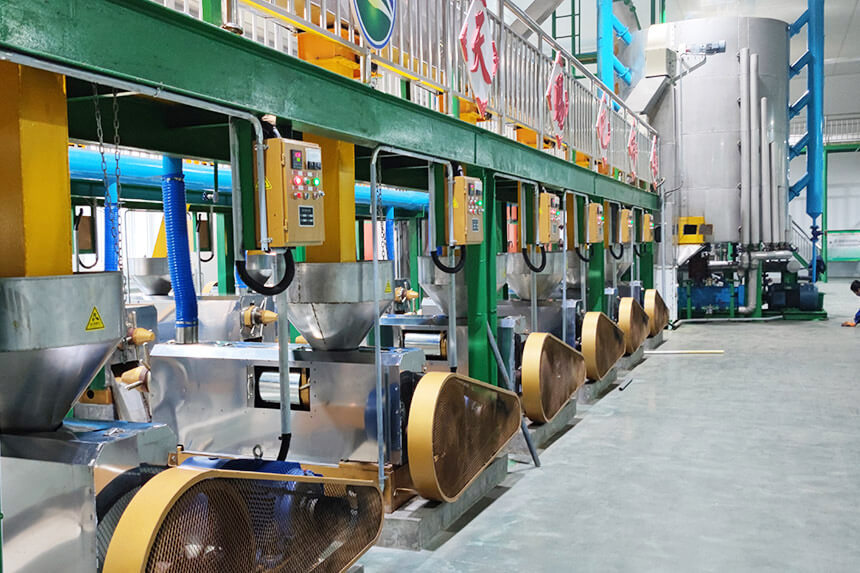
Step 3: Sesame Oil Pressing - Crude Oil Extraction
Pressing is core of sesame oil extraction process. Main have two methods: screw pressing and hydraulic pressing.
Screw Press Working Process
- Feeding section: Roasted sesame seeds are fed into pressing chamber, screw shaft pushes pressing (low-pressure pre-press).
- Pressing section: The pressing chamber space gradually decreases, pressure rise to 50–100 MPa, temperature reach 120–130°C, sesame oil flow out from gaps of pressing cage.
- Cake discharge section: Residual material is pressed into tile-shaped cake residue (thickness 1.5–2 mm, residual oil rate <7%).
![Sesame oil screw press machine for sale Sesame oil screw press machine for sale]()
Hydraulic Press Working Process (Cold Pressing)
Hydraulic pressing is called "cold pressing" too. Use hydraulic system to extract sesame oil at temperature ≤60℃ and 200-350 MPa pressure. Hydraulic pressing can retain antioxidant substances such as sesamol and retain aroma. However, oil yield is only 40%-45%, cake residual oil is as high as 15%-18%.
After pressing, crude sesame oil will precipitate and separate into solids. The oil cake can be reused as animal feed or fertilizer.
Many sesame oil processing plant use multi-stage extraction, combining screw pressing and hydraulic pressing. The first screw pressing extract most of sesame oil, second hydraulic pressing increase remaining oil cake total yield. At the same time, some plant add a third solvent extraction stage, use hexane to maximize recycle sesame oil from residue.
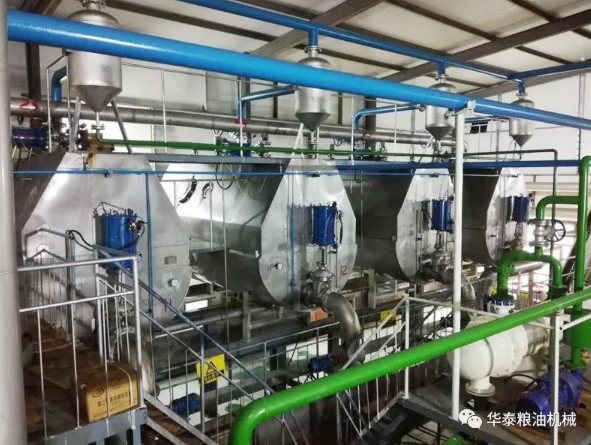
Step 4: Crude Sesame Oil Refining - Remove Impurities and Odors
After pressing, crude sesame oil has impurities like phospholipids, gums, and free fatty acids (FFAs). Refining ensures a clear, stable, and odor-free oil.
Filtering and Removing Dregs
Use plate frame filter or centrifuge to remove cake particles (particle size >50 μm solid dregs) from crude sesame oil.
This step clarifies oil, preparing it for refining.
![Sesame oil refining process Sesame oil refining process]()
Degumming (Hydration Dephosphorization)
Degumming involves heat crude sesame oil to 70–80°C, add 5–10% hot water at 80°C and stirring.
Phospholipids are separated by centrifugation after swelling with water (phospholipid content reduced to <0.1%).
Deacidification (Neutralization Free Acids)
Deacidification use sodium hydroxide (concentration 8-12°Bé) or other alkalis to neutralize free fatty acids (FFA), convert them into soapstock.
Then, centrifugal separation soapstock and use water wash until neutral (acid value ≤ 2 mg KOH/g).
Decolorization and Deodorization (optional)
Decolorization use 1%-3% activated white clay to adsorb pigments from sesame oil. The temperature is controlled at 110°C, stir for 30 minutes, filter lighten the color.
Deodorization distillate sesame oil under vacuum at 230–250°C, remove small-molecule aldehyde and ketone odors. Ensure refined sesame oil retains neutral aroma and flavor.
![Sesame oil packing process Sesame oil packing process]()
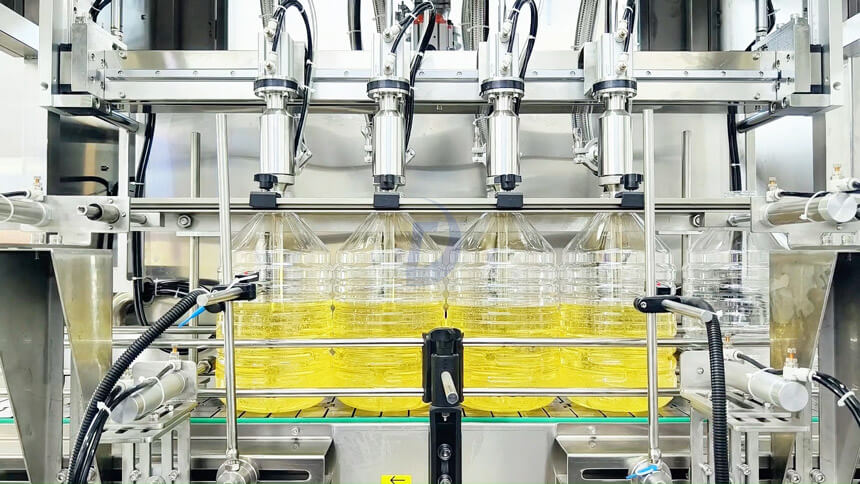
Step 5: Sesame Oil Packing
Refined sesame oil filled into bottles for retail or drums for bulk distribution. Packaging materials protect against light, heat, and air.
Quality packaging extend shelf life to 6-12 months for unopened containers, depend on processing method. Cold-pressed sesame oil have shorter shelf life than refined sesame oil. Because higher natural compounds levels, susceptible to oxidation.
Conclusion
In general, sesame oil manufacturing process includes pretreatment, steaming, pressing, refining and packaging. Each of them is very important to quality of sesame oil produced.
Henan Huatai Intelligent Equipment Group has more than 30 years of experience in manufacturing sesame oil extraction machine, and built sesame oil processing plants and complete sesame oil production lines in many countries such as India, Sudan, Myanmar, Uganda, etc. Feel free to contact us for more information about sesame oil processing.
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ