Introduction
In this article, I will introduce you to the complete canola oil solvent extraction process, the two methods of solvent extraction, the differences between pressing and solvent extraction, and the costs of establishing canola oil solvent extraction plants at different scales.
What Is Canola Oil Solvent Extraction?
Canola oil solvent extraction uses organic solvents to extract oil from canola seeds or pre-pressed canola cakes.
Its core principle is solid-liquid extraction: when oil materials contact the solvent, the oil dissolves into solvent to form mixed oil (oil-solvent mixture). Then, the system separates solvent from crude oil through evaporation and stripping, and recovers solvent in a continuous cycle.
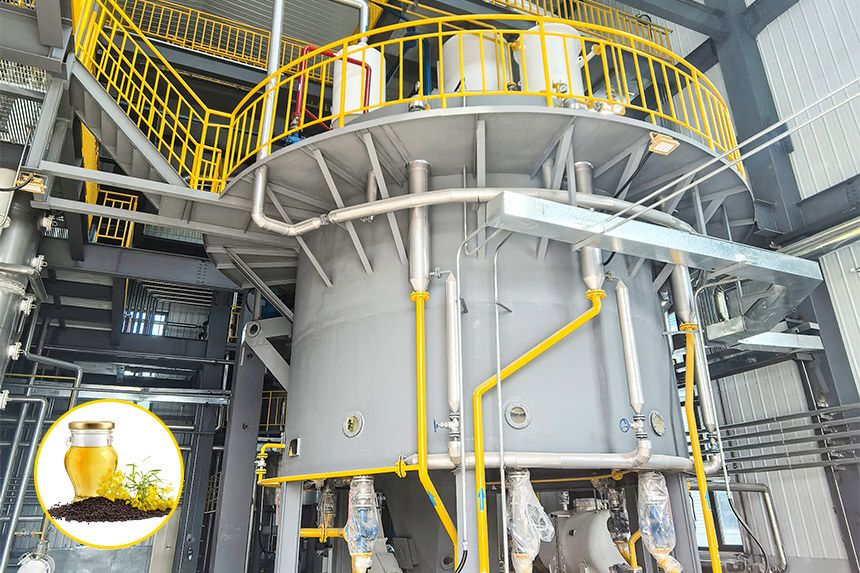
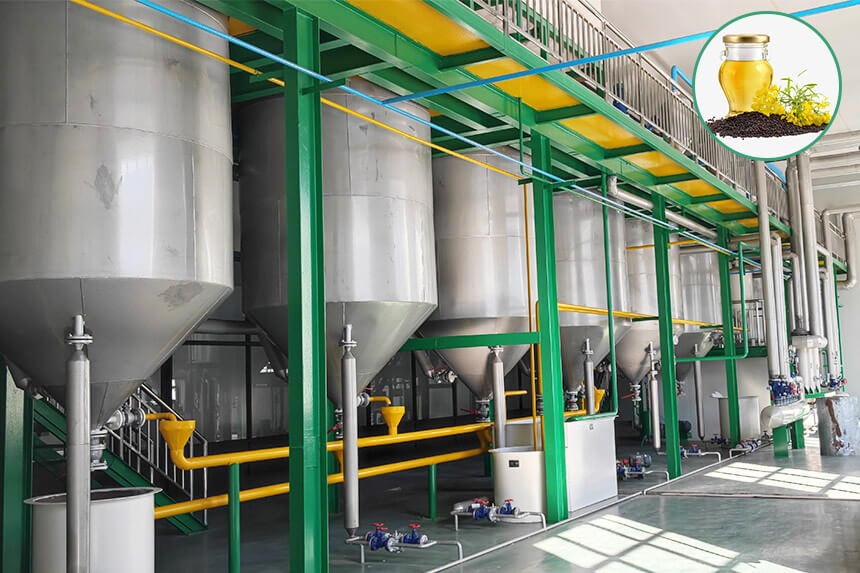
![Canola oil solvent extraction process Canola oil solvent extraction process]()
What Is Canola Oil Solvent Extraction Process?
Step 1: Canola Seed Pretreatment
- Cleaning: Remove impurities from canola seeds, reducing impurity content to ≤0.5%.
- Softening: Adjust the moisture and temperature of canola seeds to 50-60℃, with moisture content around 9%.
- Flaking: Flaking machines press canola seeds into thin flakes of 0.3-0.35mm, break down cell structures, and increase the contact area with the solvent.
- Cooking: Heat flakes and adjust the moisture content to 4-6%, raising temperature to around 110℃. This further breaks down cell structures and improves oil fluidity.
Step 2: Pre-pressing Treatment
Since canola seeds have high oil content, pre-pressing machines first extract most of the oil (pre-pressed crude oil), producing pre-pressed cake with about 12% residual oil content. Then, send cake for solvent extraction.
Step 3: Solvent Extraction
The pre-pressed canola cake passes through extractors (such as drag chain, loop or rotocel extractors) where it contacts organic solvents (such as hexane).
During this process, the extraction temperature reaches 50-55℃, flake thickness stays at ≤0.3mm, and mixed oil concentration ranges from 10-25%.
The extraction produces wet meal (containing 25-35% solvent) and mixed oil.
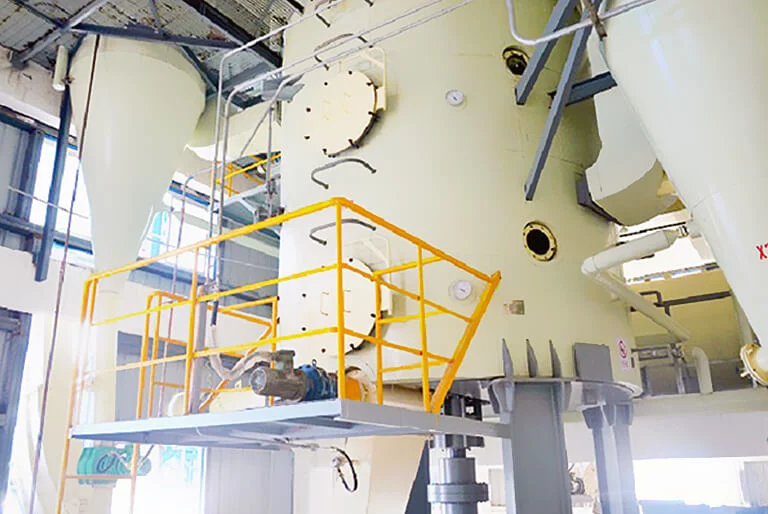
![Huatai Group DTDC desolventizer toaster Huatai Group DTDC desolventizer toaster]()
Step 4: Wet Meal Desolventizing and Drying
The wet meal goes through a desolventizer toaster (such as DTDC) to remove the solvent. The exiting meal at 105-110℃ with moisture content ≤12%, resulting in canola meal (residual oil content ≤1%).
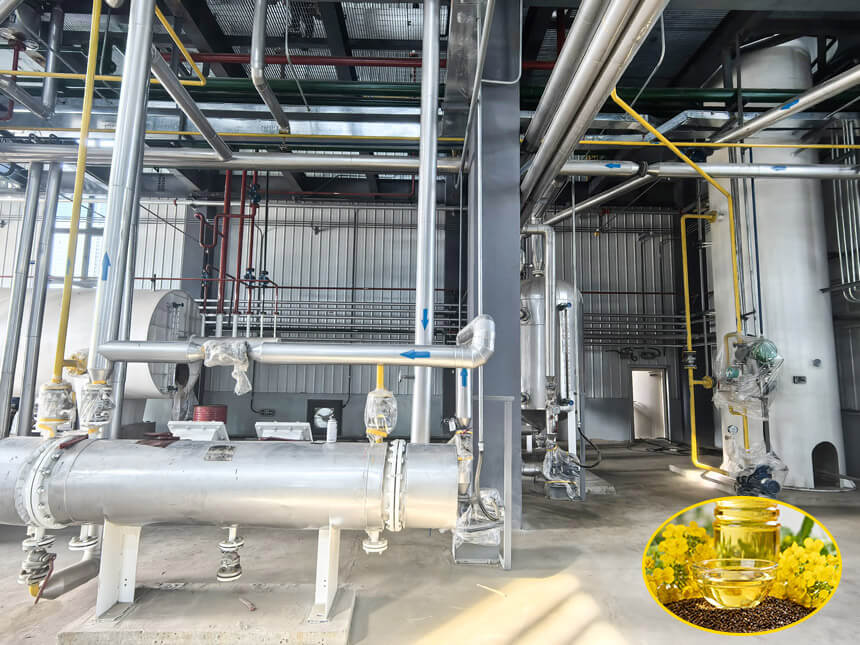
Step 5: Mixed Oil Processing
- Filtration: Removes solid meal particles from the mixed oil.
- Evaporation: Long-tube evaporators heat the mixed oil, vaporizing most solvents and increasing mixed oil concentration to over 90%.
- Stripping: A stripping tower uses steam distillation to remove residual solvent, producing extracted crude oil (solvent residue ≤0.3%).
Step 6: Solvent Recovery
All solvent vapors pass through condensation and cooling, return to the circulating solvent tank for reuse, effectively reducing production costs.
![Canola oil drag chain solvent extractor Canola oil drag chain solvent extractor]()
What Are Canola Oil Solvent Extraction Methods?
Based on the oil content of raw materials, use direct solvent extraction (suitable for low oil content materials) or pre-pressing solvent extraction (suitable for high oil content materials like canola seeds):
Method 1: Direct Solvent Extraction
After pretreatment (cleaning, flaking, cooking), the oil materials go directly to the extractor without pre-pressing.
Process flow: Canola seeds → Cleaning → Softening → Flaking → Drying/Conditioning → Direct Extraction → Wet Meal Desolventizing → Crude Oil
Key Features:
- Shorter process: Requires relatively fewer equipment.
- Oil yield: Relies entirely on solvent extraction, strict high quality flakes and extraction processes.
- Crude oil quality: Without high-temperature cooking or pressing, the crude oil has lighter color. Colloidal impurities like phospholipids lower denaturation, reduce the refining process burden. (Related Post: Canola oil refining process >>)
This method is suitable for low oil content raw materials, such as soybeans (oil content 18-20%).
Method 2: Pre-pressing Solvent Extraction
Pre-pressing solvent extraction offers an economical process for processing high oil content materials (such as canola seeds and cottonseed).
Process flow: Canola seeds → Cleaning → Softening → Flaking → Cooking → Pre-pressing → Pre-pressed Cake → Solvent Extraction → Wet Meal Desolventizing → Extracted Crude Oil + Pre-pressed Crude Oil
Key Features:
- Pre-pressing stage: Mechanical pressing extracts about 70-80% of canola oil, producing pre-pressed cake with12-18% residual oil. This pre-pressed crude oil has good quality.
- Extraction stage: Extracts remaining oil from the pre-pressed cake, reducing residual oil rate to below 1%. This reduces the extractor's load, making the scale more reasonable and economical operation.
- Highest overall efficiency: Although adding pre-pressing equipment, the "pressing + extraction" combination achieves the best balance between total investment, operating costs, and oil yield.
- Separate crude oil process: Since pre-pressed crude oil and extracted crude oil differ in quality (color, acid value, phospholipid content, etc.), store them separately and may apply different refining processes.
This method suits all high oil content materials, especially canola seeds (oil content 35-45%).
![Large-scale canola oil solvent extraction plant Large-scale canola oil solvent extraction plant]()
What Solvent Is Used for Canola Oil?
Different solvents directly affect canola oil extraction rate, quality, and production costs:
- Hexane: Widely used due to high extraction efficiency and mature technology. However, hexane comes from non-renewable resources and poses potential environmental and health hazards.
- Acetone/Ethyl Acetate Mixed Solvent: Research shows, at 2.7:1 volume ratio, extracting for 2.6 hours at 25℃ can reduce residual oil rate in canola meal to 2.18%, with phospholipid content in the oil at only 0.36%.
- Isopropanol/Cyclohexane Mixed Solvent: Patent technology shows, extracting for 20-100 minutes at 62℃ effectively reduces impurities in the oil and improves extracted oil yield.
- Other Alternative Solvents: These include methanol, anhydrous ethanol, isopropanol, acetone, and ethyl acetate, each with different extraction characteristics. However, they generally face limitations in cost, safety, or efficiency.
Canola Oil Pressing vs Solvent Extraction
| Dimension |
Pressing Method |
Solvent Extraction Method |
| Principle |
Uses mechanical pressure to press oil from seeds |
Uses organic solvents to dissolve and separate oil |
| Process Flow |
Relatively simple: Cleaning → Flaking → Cooking → Pressing |
Complex: Pretreatment → Solvent extraction → Mixed oil processing → Solvent recovery |
| Oil Yield |
Lower, with high residual oil content in meal |
High, with meal residual oil rate ≤1% |
| Product Quality |
Cold Pressing:Retains natural nutrients, good oil quality;Hot Pressing:High temperature may affect oil quality |
Crude oil requires refining to remove residual solvent; meets standards when properly refined |
| Production Cost |
Lower equipment investment, moderate energy consumption |
High equipment investment, but solvent recovery reduces material consumption |
| Production Scale |
Suitable for small to medium-scale production |
Suitable for large-scale continuous production |
| Environmental Impact |
Minimal, mainily energy consumption |
Requires strict control of solvent leakage and emissions |
| Main Applications |
Premium edible oils emphasizing flavor and nutrition |
Large-scale edible oil production; biofuel and chemical feedstocks |
Canola Oil Solvent Extraction Plant Cost Analysis
The cost of setting up a canola oil solvent extraction plant varies based on scale, automation level, and equipment brand. Here are approximate investment estimates for different scales:
| Components |
Small Plant (50 tons/day) |
Medium Plant (100-200 tons/day) |
Large Plant (300-500 tons/day) |
| Pretreatment Equipment |
$150,000 - $300,000 |
$300,000 - $600,000 |
$800,000 - $1,500,000 |
| Extraction System |
$400,000 - $600,000 |
$800,000 - $1,500,000 |
$2,000,000 - $3,500,000 |
| Evaporation Stripping System |
$100,000 - $200,000 |
$200,000 - $400,000 |
$500,000 - $900,000 |
| Solvent Recovery System |
$50,000 - $100,000 |
$100,000 - $200,000 |
$250,000 - $500,000 |
| Automated Control System |
$50,000 - $100,000 |
$100,000 - $200,000 |
$300,000 - $500,000 |
| Installation Engineering |
$100,000 - $200,000 |
$200,000 - $400,000 |
$500,000 - $1,000,000 |
| Civil and Utility Engineering |
$200,000 - $400,000 |
$400,000 - $800,000 |
$1,000,000 - $2,000,000 |
| Design and Technical Services |
$50,000 - $100,000 |
$100,000 - $200,000 |
$250,000 - $500,000 |
| Total Investment Cost |
$1.1 - $2.0 million |
$2.2 - $4.3 million |
$5.6 - $10.4 million |
Beyond the fixed asset investment above, you should also consider:
- Working capital: About 15-25% of fixed asset investment, covering raw material procurement, chemicals, labor, and operational expenses.
- Solvent consumption: Efficient plants can control solvent consumption to 1.5-3.0 kg per ton of material.
- Energy costs: Mainly including steam, electricity, and water, accounting for 25-35% of total operating costs.
- Maintenance costs: Annual maintenance expenses average 2-3% of equipment investment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, canola oil solvent extraction uses hexane to extract oil from canola seeds or pre-pressed canola cakes. Since canola seeds have high oil content, using pre-pressing followed by solvent extraction maximizes oil extraction.
Henan Huatai Intelligent Equipment Group has successful case studies of multiple canola oil processing plant projects and provides complete service processes from manufacturing to installation. If you want to establish a new canola oil production line, feel free to contact us anytime!
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ