Introduction
The canola oil refining process improves the edible quality and commercial value of canola oil. After degumming, deacidification, bleaching, and deodorization, canola oil becomes clearer and more transparent, better suited for high-temperature cooking, and lasts longer on shelf.
In this article, I will introduce you to everything about canola oil refining and the costs of establishing refineries at different scales.
What Is Refined Canola Oil?
Refined canola oil is an edible oil produced from crude canola oil through pressing or solvent extraction. It through a series of physical and chemical treatments to remove impurities, gums, free fatty acids, pigments, off-flavors, and other non-triglyceride components. The result meets human consumption standards.
Research shows, refined canola oil is categorized into four grades based on refinement level: Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3, and Grade 4.
Grade 1 canola oil must contain moisture and volatile matter ≤0.05%, insoluble impurities ≤0.05%, acid value (KOH) ≤0.2mg/g, and peroxide value ≤5.0mmol/kg. In addition, no detectable solvent residues.
![What is refined canola oil What is refined canola oil]()
Why Does Canola Oil Need to Refining?
Because Unrefined crude canola oil contains many components that harm human health and processing. These impede people direct consumption and commercial applications. Here are some safety hazards in unrefined canola oil:
High Harmful Substance Content
Unrefined canola oil contains erucic acid levels ranging from 20% to 60%. Research shows that feeding young mouse a diet containing 45% erucic acid causes fat deposits and fibrous tissue formation in their heart muscle. In addition, crude oil may contain trace harmful substances like glucosinolates.
Excessive Free Fatty Acids
When crude oil contains too much free fatty acid, it accelerates oil rancidity and produces peroxides. Long-term consumption speeds up human aging and carries cancer risks.
Phospholipids and Colloids
Unrefined canola oil contains high phospholipid levels. When heating, it foams and smokes, increasing the risk of lung cancer during cooking. High temperatures during frying also create brown substances that affect food's sensory quality.
Pigments and Off-Flavors
Pigments in crude oil not only affect sensory quality, but chlorophyll also destabilizes the oil and promotes photo-oxidation reactions. In addition, sulfur-containing compounds in crude oil produce grassy and pungent taste that affect flavor.
What Is Canola Oil Refining Process?
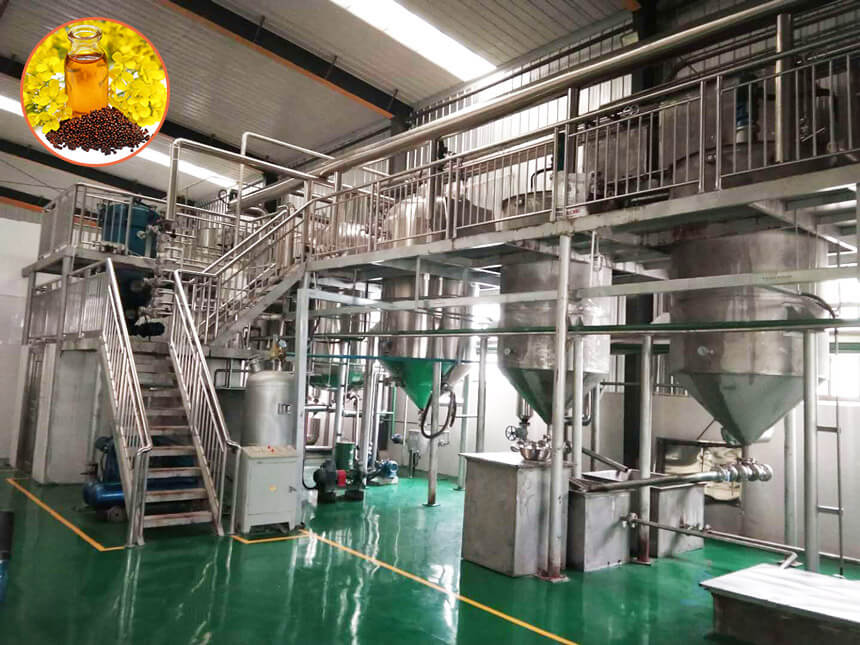
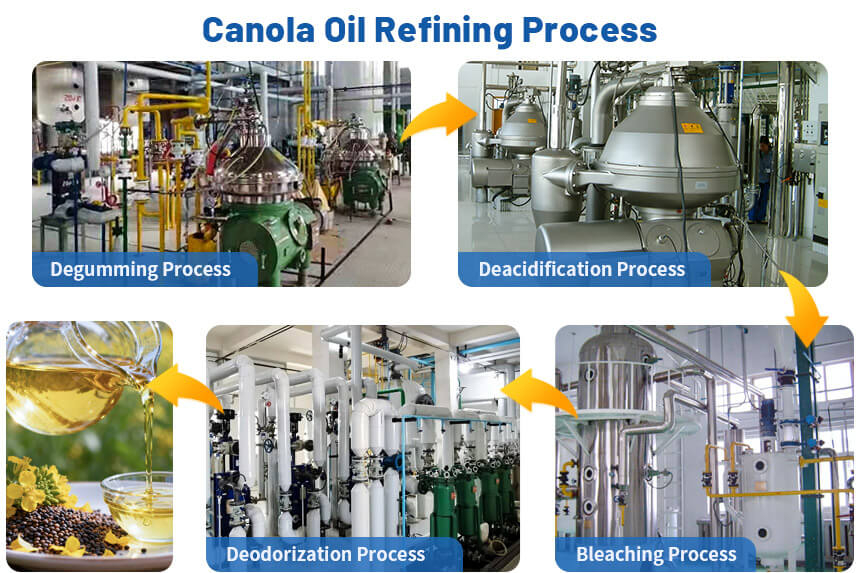
The canola oil refining process transforms crude canola oil into edible oil suitable for direct human consumption through degumming, deacidification, bleaching and deodorization. Canola oil refining plant uses continuous and automated production processes to ensure stable product quality and improved production efficiency. Here's the complete refining process:
![Rapeseed oil refining process flow chart Rapeseed oil refining process flow chart]()
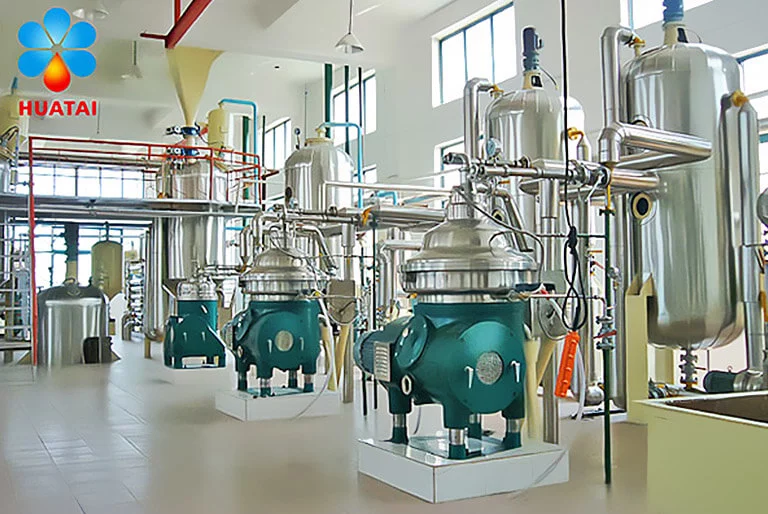
Degumming Process
Degumming removes colloidal impurities like phospholipids, mucilage, and proteins from crude canola oil. These impurities affect the effectiveness of subsequent refining steps and the final product's stability.
Working Principle
This process utilizes the hydrophilic nature of colloidal impurities like phospholipids. Add hot water or phosphoric acid to crude oil, which causes the gums absorb water, swell, and coagulate. Then, centrifugal separation or sedimentation removes them.
Henan Huatai Intelligent Equipment Group combines degumming with alkali refining. First, remove impurities from crude canola oil, heat it to 65-80°C, then add sodium hydroxide solution to obtain degummed alkali-refined oil.
Technical Parameters
Control hydration degumming temperature at 65-80°C, adding water at 2-3 times the phospholipid content in crude oil. Stir for about 30 minutes, then send the mixture to a centrifuge to separate gums.
For non-hydrated phospholipids, must first add 0.1%-0.2% phosphoric acid for acidification treatment, converting them to hydrated phospholipids before performing hydration degumming.
Equipment Configuration
The degumming process requires main equipment including reaction tanks, centrifuges, and heating systems. Reaction tanks need variable-speed stirring devices to ensure thorough mixing of water and crude oil. Self-cleaning centrifuges enable continuous production. The heating system uses plate heat exchangers to improve thermal efficiency.
![Huatai Group edible oil neutralization tank Huatai Group edible oil neutralization tank]()
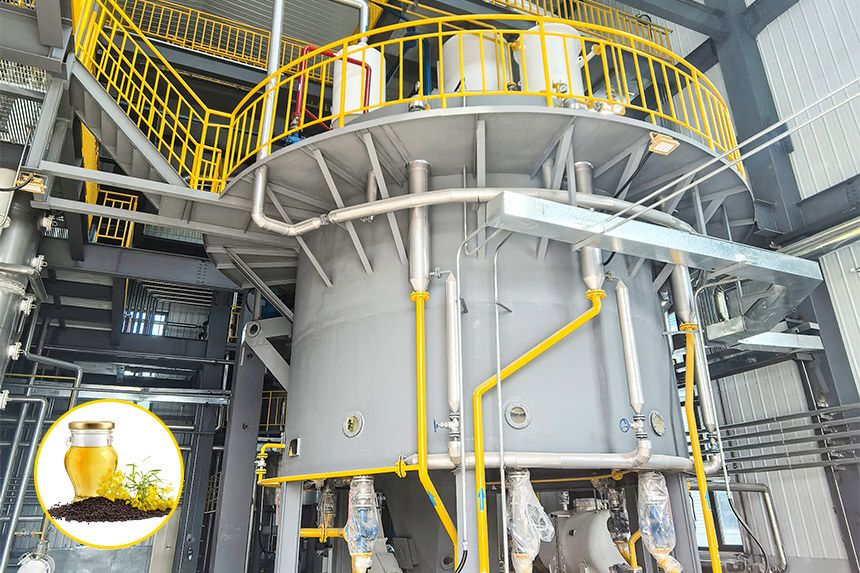
Deacidification Process
Deacidification removes free fatty acids from crude canola oil while removing residual phospholipids and pigments. It mainly involves two methods: chemical deacidification and physical deacidification.
Chemical Deacidification: Add food-grade sodium hydroxide to crude oil, neutralize free fatty acids and produce soapstock. Then, centrifugal separation removes it. The neutralization reaction at 75-85°C. After the reaction, centrifugal separation of the oil-soap mixture yields deacidified oil.
Physical Deacidification: Also called steam distillation deacidification, use the volatility difference between free fatty acids and triglycerides. Under 1-3mbar and 240-260°C, steam carries out free fatty acids. This method avoids chemical reagents, reduces wastewater discharge, and is particularly suitable for refining crude oil with high acid values. Henan Huatai Group's cold-refined canola oil fully automatic high-efficiency extraction method uses physical deacidification technology, reducing alkali refining losses.
Chemical deacidification has lower investment and suits crude oil with various acid values, but produces soapstock and wastewater. Physical deacidification yields higher product recovery without chemical contamination, but need greater equipment investment and higher energy consumption. For large-scale continuous canola oil processing plants, physical deacidification offers more advantages.
![Huatai Group edible oil deacidification tower Huatai Group edible oil deacidification tower]()
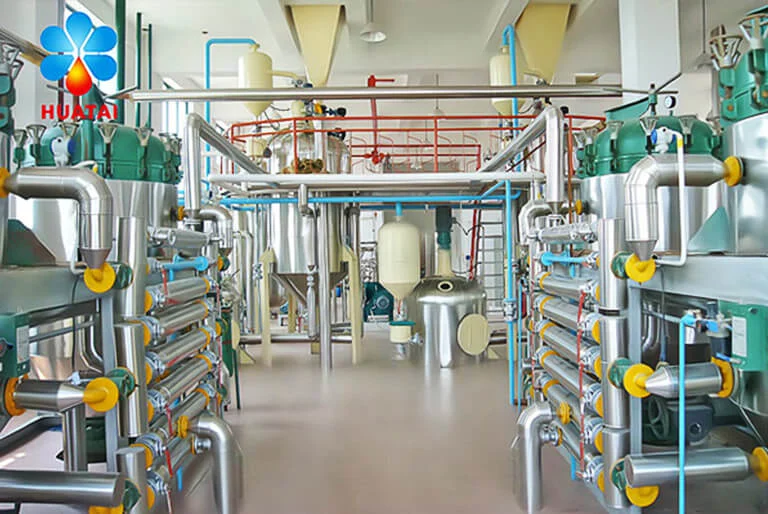
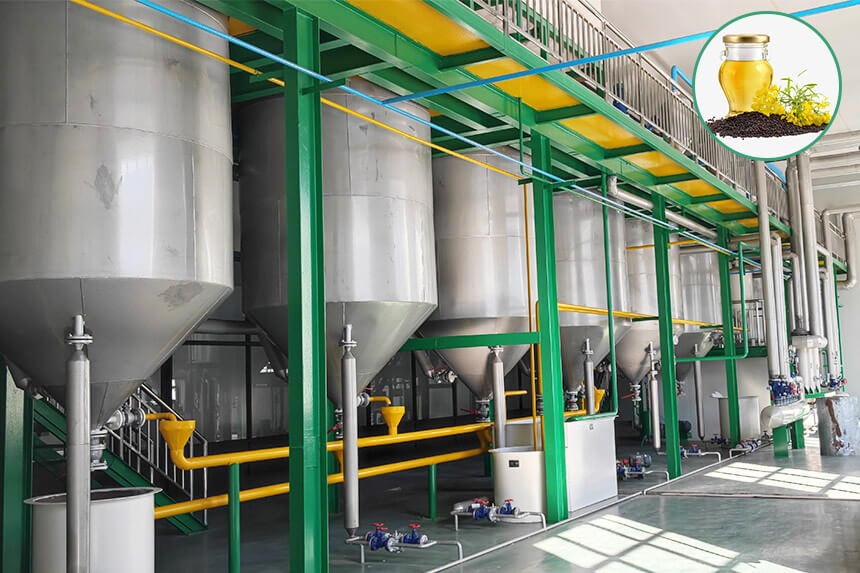
Bleaching Process
Bleaching is through adsorption, not only removing pigments from crude oil but also comprehensively improving the oil's color, oxidative stability, and flavor.
- Adsorption Principle: Use adsorbents like activated clay and activated carbon to remove pigments such as chlorophyll and carotenoids from crude canola oil, while further removing residual phospholipids, saponins, and oxidation products. Add activated clay at 1%-3% of oil weight, increasing the amount appropriately for darker crude oil.
- Process Conditions: Bleaching is under vacuum conditions at temperatures controlled at 120-125°C for about 15-30 minutes. Vacuum can prevent oil oxidation during heating.
- Adsorbent Selection: Activated clay is the most commonly used adsorbent, with strong adsorption capacity for chlorophyll. For removing red pigments, use small amounts of activated carbon (about 10%-30% of clay amount). Spent clay contains about 20%-40% oil, requires recovery processing to reduce production costs and environmental pollution.
![Huatai Group edible oil decolorization tower Huatai Group edible oil decolorization tower]()
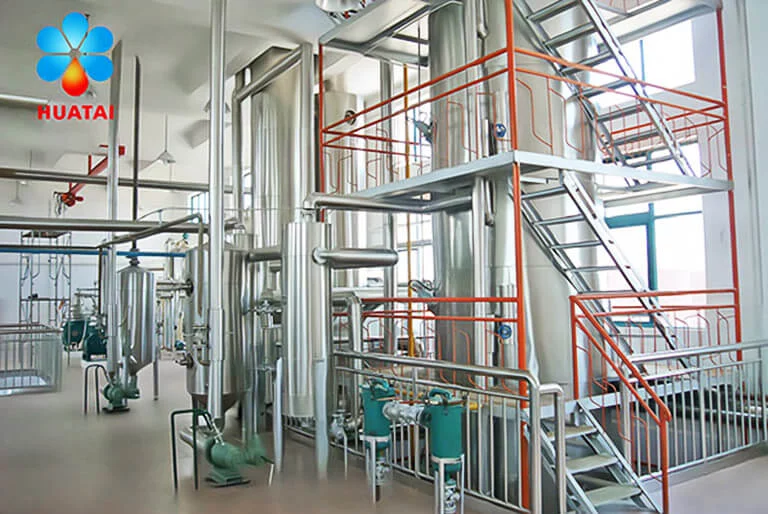
Deodorization Process
Deodorization removes volatile substances causing off-flavors and odors in crude canola oil, such as aldehydes, ketones, and hydrocarbons, while improving the oil's smoke point and oxidative stability.
- Working Principle: Based on steam distillation principles, inject direct steam under 1-3mbar and 260-290°C, and carry out volatile off-flavor substances from the oil. The deodorization process also decomposes trace heat-sensitive substances, improving oil flavor and color.
- Process Parameters: Deodorization temperature ranges from 260-290°C, with oil remaining in the deodorization tower for 1-1.5 hours. To prevent oil oxidation, must strictly control direct steam quality and amount.
- Heat Recovery: Huatai Group's continuous deodorization system includes a complete heat recovery device. Deodorized hot oil exchanges heat with incoming cold oil, recovering about 80% of heat and reducing steam consumption. The system recovers fatty acids and volatile substances produced during deodorization through condensation, avoiding environmental pollution from direct discharge.
![Set up canola oil refinery plant Set up canola oil refinery plant]()
Is Refined Canola Oil Healthy?
Moderately refined canola oil retains most nutrients beneficial to humans while removing harmful substances, offering good health value.
Refined canola oil contains rich monounsaturated fatty acids (oleic acid) and linoleic acid, and also certain amounts of α-linolenic acid, which benefit human cardiovascular and cerebrovascular health.
For babies and young children, their bodies have lower enzyme activity for breaking down erucic acid. So, choosing low-erucic acid refined canola oil is safer.
Refined Canola Oil Vs Unrefined Vs Cold Pressed.
Different types of canola oil show differences in physical and chemical properties, nutritional components, and application due to their different processing methods. Here are the differences between refined canola oil, unrefined canola oil, and cold pressed canola oil: (Related Post: Canola oil vs mustard oil >>)
| Indicators |
Refined Canola Oil |
Unrefined Canola Oil |
Cold Pressed Canola Oil |
| Processing Method |
Multiple physical and chemical refining steps (degumming, deacidification, bleaching, deodorization) |
Simple pressing followed by sedimentation or filtration |
Low-temperature pressing below 65°C, physical filtration only |
| Processing Temperature |
Deodorization reaches 260-290°C |
Seed roasting can reach 120-180°C |
<65°C |
| Chemical Reagents |
May use sodium hydroxide, clay, etc. |
None |
None |
| Color |
Clear and transparent, light yellow |
Deep yellow or brownish-red, possibly cloudy |
Bright color, good appearance |
| Flavor |
Light, no off-flavors |
Strong characteristic rapeseed smell, possibly "green taste" |
Retains natural rapeseed aroma |
| Smoke Point |
High (≥220°C, typically 220–240°C) |
Low (160–180°C) |
Medium (190–210°C) |
| Stability |
High oxidative stability, long shelf life |
Easily oxidizes and becomes rancid, short shelf life |
Oxidative stability between the two |
| Free Fatty Acids |
Low content (≤0.2%) |
High content, easily becomes rancid |
Moderate content |
| Phospholipid Content |
Extremely low (≤0.05%) |
High (1%-3%) |
Moderately low (0.1%-0.8%) |
| Erucic Acid Content |
Low erucic acid (≤3%-5%) |
May reach 20%-60% |
Depends on raw materials, requires low-erucic varieties |
| Vitamin E |
Partial loss (about 500.96mg/kg) |
Relatively well preserved |
Retains over 80% (723.94mg/kg) |
| Phytosterols |
Partial loss |
Completely preserved |
Relatively well preserved |
| Polyphenols |
Significant loss (47.33mg GAE/kg) |
Completely preserved |
Relatively well preserved (54.08mg GAE/kg) |
| Residual Impurities |
Minimal |
May contain mechanical impurities, gums, etc. |
Small amount |
| Harmful Substances |
Essentially removed |
May contain trace amounts of glucosinolates, etc. |
No chemical residue |
| Application |
Mass catering, food industry, home cooking |
Traditional flavor dishes, specific consumer groups |
Health-conscious consumers, high-end catering |
Canola Oil Refinery Plant Cost Analysis.
Establishing a canola oil refinery plant needs rational planning of production scale based on factors like raw material supply, financial strength, target market, and expected returns. Here's an investment cost analysis for three common refinery scales:
| Investment Factors |
Batch (1-10 tons/day) |
Semi-Continuous (10-30 tons/day) |
Fully Continuous (30-100 tons/day) |
| Equipment Cost |
$50,000-$150,000 |
$150,000-$400,000 |
$400,000-$1,000,000 |
| Plant Area |
200-500m² |
500-1,000m² |
1,000-2,500m² |
| Energy Cost |
$40-60/ton |
$30-50/ton |
$20-40/ton |
| Labor |
3-5 people |
8-15 people |
20-40 people |
| Automation Level |
Low, mainly manual control |
Medium, partially automated control |
High, fully automated control |
| Production Process |
Batch production, quality fluctuates significantly |
Main processes continuous, some batch |
Fully continuous production, stable quality |
| Construction Period |
2-4 months |
4-8 months |
8-12 months |
| Raw Material Adaptability |
Multi-variety small-batch production |
Medium-scale production |
Single-variety large-scale production |
| Product Quality |
Average, limited consistency |
Good, relatively high consistency |
Excellent, high stability |
| Comprehensive Cost |
$55–82/ton |
$41–68/ton |
$27–55/ton |
| Investment Recovery Period |
3-5 years |
4-6 years |
5-7 years |
Conclusion
Above, you will find everything about the canola oil refining process. Canola oil refining projects face multiple challenges including technical risks, market risks, and policy risks, making it very important to choose an experienced and reliable equipment supplier.
Henan Huatai Group has over 37 years of experience in researching and manufacturing canola oil production line. Our engineers can customize professional solutions for you. Feel free to contact us or visit our factory anytime!
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ




















