1. Purpose of soybean oil refining
Remove impurities: remove suspended solids such as colloids, phospholipids, and proteins.
Reduce free fatty acids (FFA): prevent oil oxidation and rancidity, and extend shelf life.
Decolorization: remove pigments such as chlorophyll and carotene to improve the color of oil products.
Deodorization: eliminate beany odor, odor of free fatty acids and other volatile substances.
Improve safety: inactivate harmful substances (such as peroxides) produced by oxidation and deterioration.

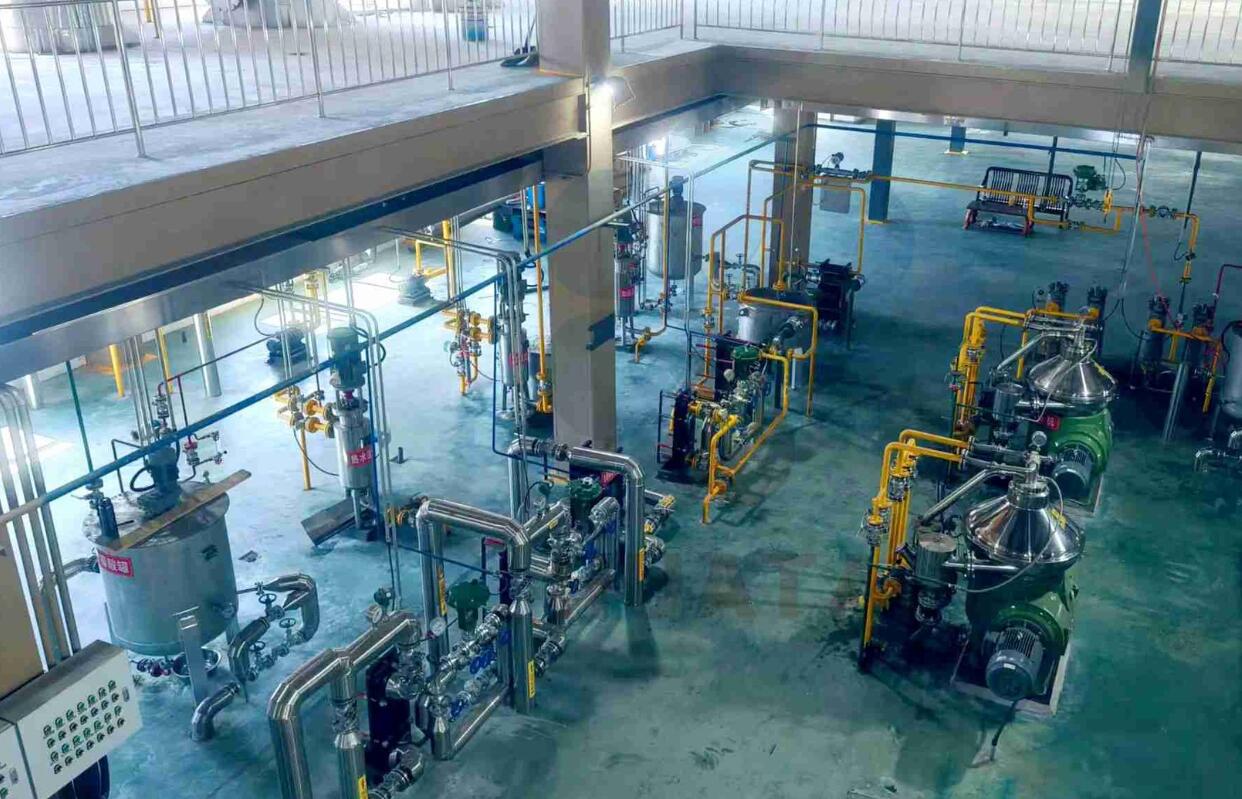
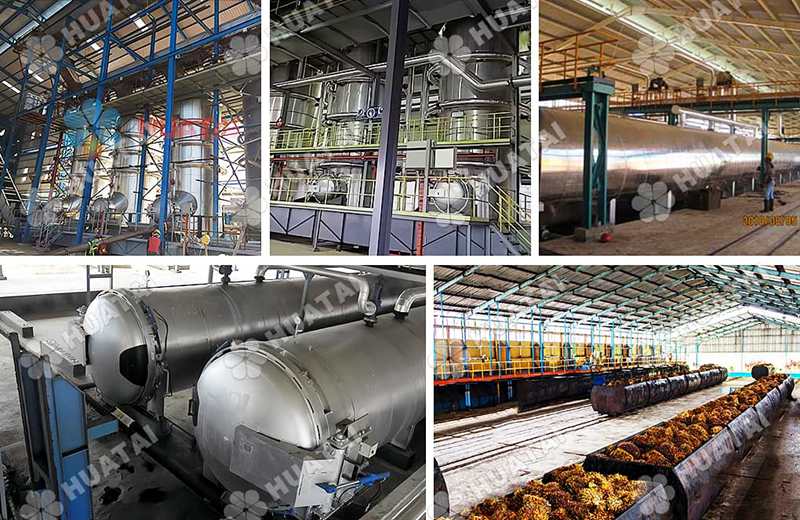
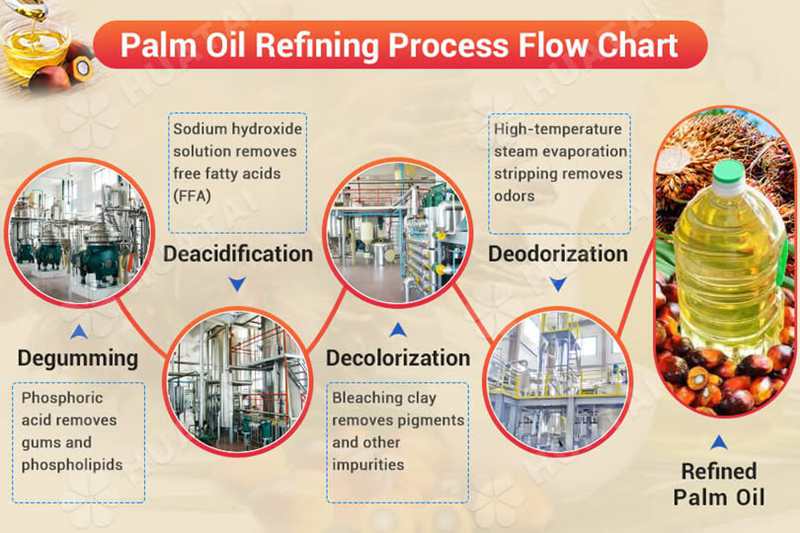
2. Soybean Oil Refining process
Soybean oil refining is usually divided into physical refining and chemical refining, which are often used in combination in actual production.
1. Pretreatment Filtration: remove large particles of impurities (such as bean dregs, mud and sand).
Alkali refining (chemical degumming):
Add sodium hydroxide solution to neutralize free fatty acids (to form soap stock).
Remove colloid-soluble impurities (such as phospholipids and proteins).
2. DecolorizationAdsorption decolorization: Use white clay (such as activated white clay, attapulgite) to adsorb pigments and residual impurities.
High temperature decolorization: Heat under vacuum conditions to accelerate the decomposition of pigments.
3. DeodorizationSteam distillation: Steam is introduced at high temperature (230-260℃) and high vacuum (0.1-1 mmHg) to remove volatile odor substances (such as aldehydes and ketones).
4. Dewaxing (optional)Centrifugation after freezing to remove wax and improve low-temperature fluidity.
5. Physical refining (alternative/supplementary to chemical refining)
Molecular distillation: Use molecular distillation technology to directly separate free fatty acids and retain more natural vitamin E.
 3. The impact of refining on oils and fats
3. The impact of refining on oils and fatsIndicators Unrefined oil Refined oil
Free fatty acids (FFA) Higher (easy to oxidize and become rancid) ≤0.1% (high stability)
Color Dark yellow or green Light yellow or colorless
Smell Obvious beany smell Tasteless or light
Vitamin E content More retained Partial loss (especially high-temperature refining)
Oxidative stability Poor Significantly improved
4. Advantages and disadvantages of refined oilsLong shelf life: Reduced free fatty acids and impurities, delayed oxidation.
Wide applicability: Suitable for high-temperature cooking (such as frying).
High safety: Reduces the residue of harmful substances such as aflatoxin.
Designed for efficiency, these machines cater to various
edible oil refinery plant needs. Suitable for soybean oil refining, peanut oil refinery, sunflower seeds oil refining etc. Professional Edible Oil Refinery Machine, choose Henan Huatai group.
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ