Introduction
Cottonseed oil is one of the world's main vegetable oils. It's a clear transparency, mild flavor, high smoke point, and excellent stability. It is a premium ingredient for cooking, and food processing has high value.
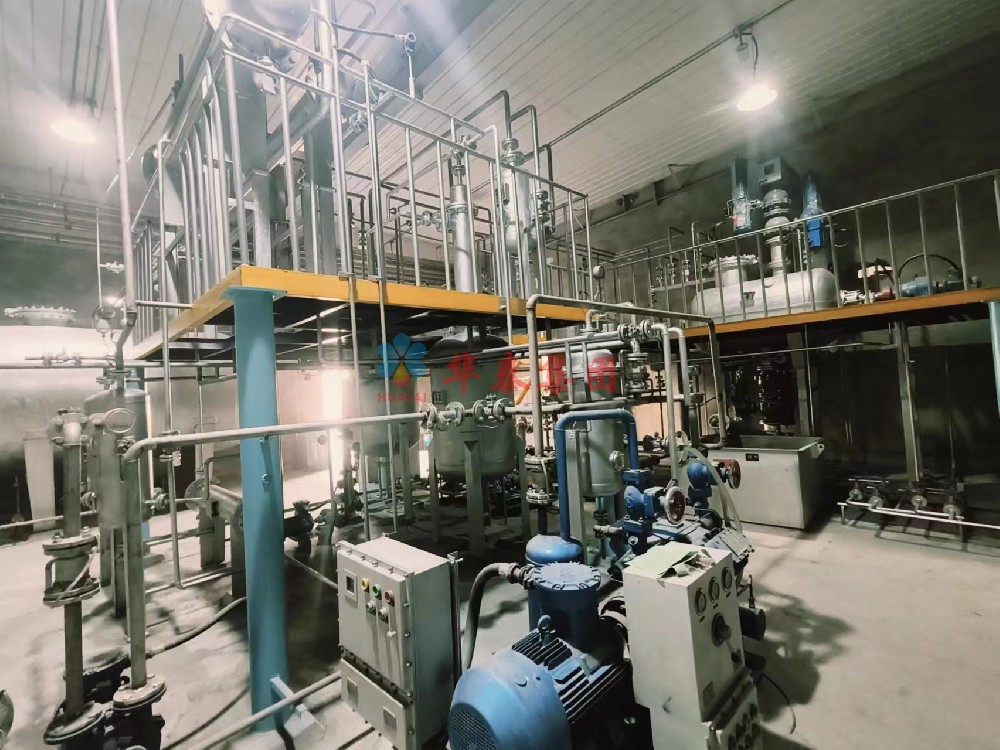
Henan Huatai Group has 37 years of experience designing and building edible oil plants for global clients. We can help you establish a technologically advanced, highly profitable modern cottonseed oil refinery plant.
What is Refined Cottonseed Oil?
Refined cottonseed oil with cotton seeds as raw material. Degumming, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization result in edible oil suitable for human consumption. It appears orange-yellow or brown, clear and transparent.
Refined cottonseed oil contains a balanced fatty acid composition: palmitic acid (21.6%-24.8%), stearic acid (1.9%-2.4%), oleic acid (18.0%-30.7%), and linoleic acid (44.9%-55.0%).
![Cottonseed oil refining process flow chart Cottonseed oil refining process flow chart]()
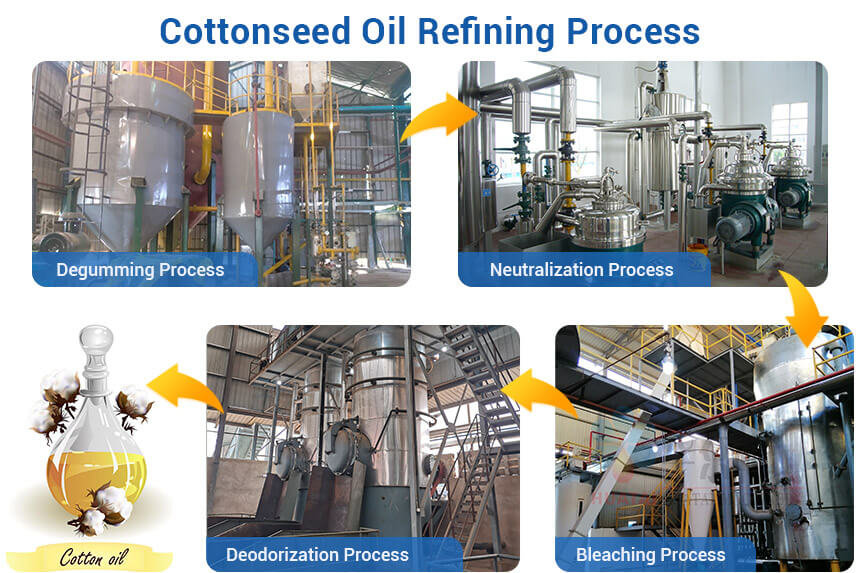
What Is the Process of Refining Cottonseed Oil?
Degumming
Degumming removes phospholipids, mucilage, and other colloidal impurities from crude cottonseed oil. Traditional degumming uses water hydration: adding hot water causes phospholipids and gums to absorb water, swell, coagulate, and separate. Modern refining processes use phosphoric acid pretreatment, which effectively decomposes and coagulates non-hydratable phospholipids, improving degumming efficiency.
During degumming, temperature, water addition volume, and stirring speed all directly affect results. Incomplete degumming leads to problems like emulsification in subsequent processes.
Neutralization
Neutralization is also called alkali refining and deacidification, removes free fatty acids from crude cottonseed oil. Free fatty acids cause oil rancidity and produce astringent taste while affecting the oil's smoke point and stability. The neutralization process works by reacting free fatty acids with alkali solution (sodium hydroxide) through saponification, producing soapstock and water.
Key parameters for neutralization include alkali solution concentration, excess alkali amount, reaction temperature, and stirring conditions. Research shows, optimal process conditions for cottonseed oil neutralization involve: adding 0.02% phosphoric acid (by oil weight) for pretreatment, then adding alkali solution with 1.0% excess alkali for alkali refining. Alkali solution concentration based on crude oil acid value, generally controlling between 20-28°Bé. Operating temperature typically stays at 25-30℃, with final temperature controlled at 60-65℃.
After neutralization, centrifugal separation removes soapstock. Then add 12% (of oil volume) soft water at 85℃ for washing to thoroughly remove residual soap particles. After washing, dehydrate at 130℃ under 0.098 MPa vacuum for 30 minutes to ensure moisture content meets standards.
![Henan Huatai Group edible oil neutralization tank Henan Huatai Group edible oil neutralization tank]()
Bleaching
Bleaching removes pigment substances from cottonseed oil, especially gossypol and its derivatives, enhancing appearance quality. The bleaching process uses adsorption bleaching, utilizes adsorbents (activated clay) to selectively adsorb pigments.
Research shows, optimal bleaching conditions for cottonseed oil involve continuous double bleaching at 105℃ under 0.098 MPa vacuum, adding 2% clay (based on oil weight) each time. This process fully utilizes clay's bleaching effect, reducing clay usage while minimizing refining loss. Control bleaching time to around 20 minutes.
After bleaching, need to filter out residual clay. Keep oil temperature during filtration below 70℃ to ensure filtering effectiveness and prevent oil oxidation.
![Henan Huatai Group edible oil decolorization tower Henan Huatai Group edible oil decolorization tower]()
Deodorization
Deodorization removes volatile substances that cause off-flavors and oxidation in cottonseed oil, including aldehydes, ketones, hydrocarbons, and other compounds, improving cottonseed oil flavor and stability. The deodorization principle relies on steam distillation—under high temperature and high vacuum conditions, steam carries away off-flavor substances.
The cottonseed oil deodorization process conditions are at 210℃ under 1kPa vacuum. Some processes use lower temperatures (around 180℃) and vacuum (666.6-1.333Pa), with the entire deodorization process lasting 5-7 hours.
More advanced processes use high-temperature short-time deodorization, controlling temperature around 250℃ for 2-3 hours. However, deodorization tower materials must be made of stainless steel to prevent metal ions from catalyzing oil oxidation at high temperatures.
During deodorization, add trace amounts of citric acid (0.02%-0.04%), preparing it as a 5% aqueous solution before use. Citric acid chelates metal ions that promote oxidation, improving oil oxidation stability and storage period. Deodorized cottonseed oil should be clear and transparent, retaining cottonseed oil's characteristic mild flavor without off-odors.
![Henan Huatai Group edible oil deodorizing tower Henan Huatai Group edible oil deodorizing tower]()
Winterization (Optional)
Winterization is an optional process in cottonseed oil refining. It removes high-melting-point components, such as saturated triglycerides and waxes. Cottonseed oil contains 20%-30% homoacid triglycerides, whose fatty acids have relatively high freezing points. During low-temperature storage, these homoacid triglycerides precipitate from the oil, causing cloudiness or sediment that affects oil appearance.
The winterization process achieves separation through controlled cooling crystallization and filtration. Cool deodorized cottonseed oil to a specific temperature, causing high-melting-point components to crystallize and precipitate. Then keep temperature to promote crystal growth, finally separating crystalline material through filtration. Research shows, cottonseed oil treated with freeze filtration to remove sediment solidifies only at 0°C.
Winterized cottonseed oil also called salad oil, shows significantly improved cold storage stability, making it suitable for refrigerated foods and salad dressings. Whether to perform winterization depends on the product's target market and uses.
![Henan Huatai Group edible oil crystallization tank Henan Huatai Group edible oil crystallization tank]()
Why Does Cottonseed Oil Need Refining?
Cottonseed oil requires refining primarily for safety and eating quality. Crude cottonseed oil contains various substances harmful to human body, most is gossypol. Research shows, gossypol exhibits considerable toxicity to the liver, blood vessels, intestines, and nervous system. According to health standards, edible oil must contain less than 0.02% gossypol.
Beyond gossypol, crude cottonseed oil also contains phospholipids, gums, waxes, and other impurities. These substances affect the oil's transparency and stability, causing cloudiness and sediment during storage. Refining can remove these impurities.
So, cottonseed oil must go through refining before people can consume it directly.
Is Refined Cottonseed Oil Safe?
Yes, refined cottonseed oil is a safe edible oil. Refining not only removes harmful substances like gossypol but also enhances the oil's quality and stability. The human body digests and absorbs refined cottonseed oil at a 98% rate, making it safe for consumption.
Refined cottonseed oil offers not just safety but also nutritional and health value. Cottonseed oil contains large amounts of linoleic acid (44.9%-55.0% content)—an essential fatty acid for humans. It effectively inhibits cholesterol rise in blood, maintaining cardiovascular health.
Refined Vs Unrefined Cottonseed Oil
The table below compares refined and unrefined cottonseed oil across multiple aspects including processing methods, physical characteristics, and chemical properties:
| Indicators |
Refined Cottonseed Oil |
Unrefined Cottonseed Oil |
| Processing Method |
Through a complete refining process including degumming, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization, possibly including winterization |
Through only simple pressing, sedimentation or filtration |
| Appearance and Color |
Orange-yellow or brown, clear and transparent |
Brownish-yellow or dark brown, cloudy and opaque |
| Odor and Taste |
Characteristic cottonseed oil aroma, no off-odors, mild taste |
Acrid and astringent taste, pungent flavor |
| Low-Temperature Stability |
Does not solidify at 0°C after winterization |
Develops cloudiness and flocculent sediment at low temperatures |
| Smoke Point |
≥215°C |
Lower, produces heavy smoke during cooking |
| Gossypol Content |
≤0.02% |
About 1% |
| Acid Value |
≤0.2 mgKOH/g |
>3.0 mgKOH/g |
| Peroxide Value |
≤5 mmol/kg |
Elevated peroxide value, prone to oxidation and deterioration |
| Fatty Acid Composition |
Retains beneficial fatty acids, linoleic acid content 44.9-55.0% |
Similar fatty acid profile, but prone to hydrolysis producing higher free fatty acids |
| Impurities Contains |
Minimal phospholipids, colloids, waxes, and other impurities |
Large amounts of phospholipids, colloids, proteins, mucilage, and other impurities |
| Stability |
Good oxidation stability, long shelf life |
Poor stability, prone to rancidity |
Cottonseed Oil Refinery Plant Investment Cost Analysis
Establishing a cottonseed oil refinery plant requires planning investment based on expected production scale, automation level, and product quality requirements. Below are investment cost structures for three common scales (batch, semi-continuous, fully continuous):
| Cost Item |
Batch (1-10 tons/day) |
Semi-continuous (10-30 tons/day) |
Fully continuous (30-100 tons/day) |
| Pretreatment Equipment |
$25,000-$50,000 |
$75,000-$150,000 |
$200,000-$450,000 |
| Neutralization System |
$35,000-$70,000 |
$100,000-$200,000 |
$300,000-$600,000 |
| Bleaching System |
$20,000-$40,000 |
$60,000-$120,000 |
$150,000-$300,000 |
| Deodorization System |
$40,000-$80,000 |
$120,000-$240,000 |
$350,000-$700,000 |
| Winterization System (Optional) |
$15,000-$30,000 |
$45,000-$90,000 |
$120,000-$240,000 |
| Factory Buildings and Civil Engineering |
$30,000-$60,000 |
$90,000-$180,000 |
$250,000-$500,000 |
| Installation and Commissioning |
$28,000-$60,000 |
$89,000-$178,000 |
$248,000-$506,000 |
| Total Investment |
$198,000-$420,000 |
$624,000-$1,248,000 |
$1,738,000-$3,536,000 |
Beyond the direct investment costs listed in the table, you must also consider operating costs, including raw material procurement, chemical consumption, energy and power, labor and maintenance. Research shows, consumption during cottonseed oil refining mainly includes:
- Clay consumption: about 2%-5%
- Alkali solution usage: determined by crude oil acid value
- Steam consumption: about 300-600 kg/ton of cottonseed oil
- Electricity consumption: about 20-50 kWh/ton of cottonseed oil
Conclusion
Through the content above, you now understand the process, safety logic, and investment scale of cottonseed oil refining. When investing in a cottonseed oil refinery plant, selecting an experienced and trustworthy supplier is very important.
Henan Huatai Intelligent Equipment Group provides turnkey cottonseed oil production line projects covering project consultation, process design, core equipment manufacturing, complete plant installation and commissioning, personnel training, and after-sales support. We commit to customizing optimal solutions for you from batch to fully continuous operations. Feel free to contact us anytime!
![]() Service Coverage
Service Coverage
![]() FAQ
FAQ